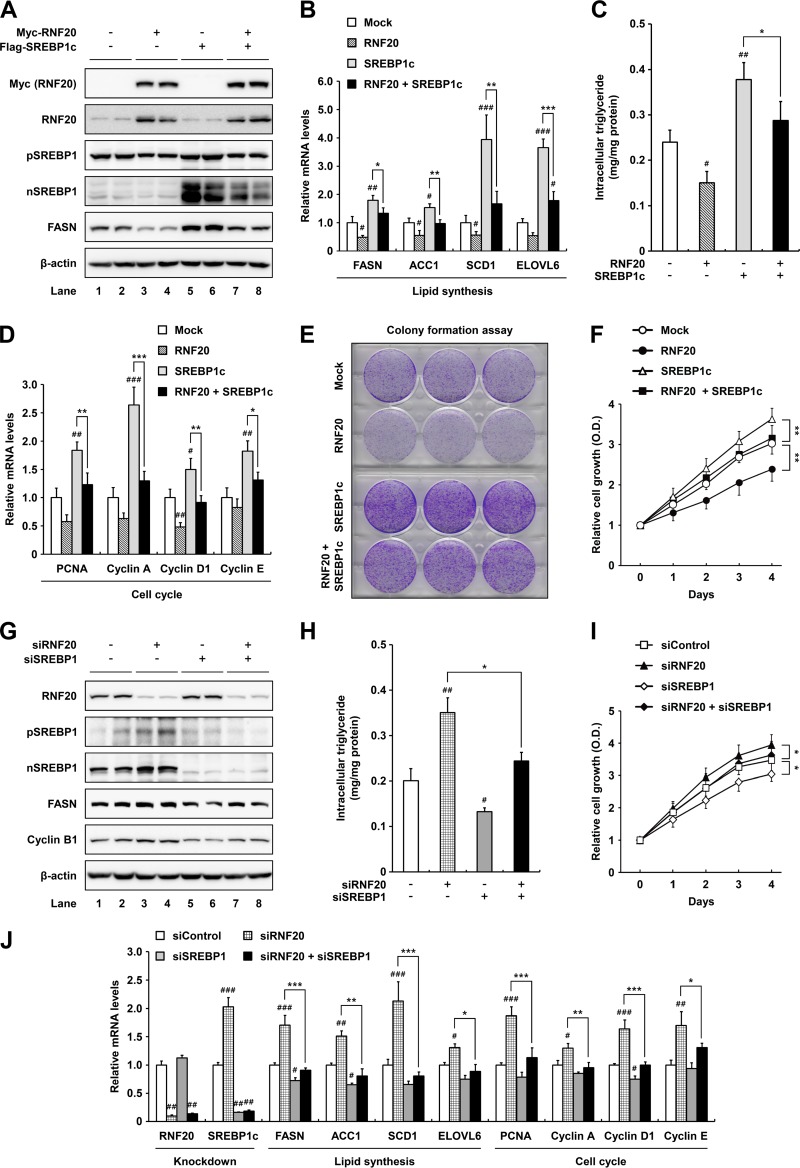
FIG 3.
RNF20 represses ccRCC cell proliferation by inhibiting SREBP1. (A) ACHN ccRCC cells were infected with adenovirus containing Myc-RNF20 and/or Flag-SREBP1c. After infection, total cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting. pSREBP1, precursor SREBP1; nSREBP1, nuclear SREBP1. (B) ACHN ccRCC cells were transduced with lentivirus for stable overexpression of RNF20 and/or SREBP1c. Relative mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR. (C) Intracellular triglyceride contents were measured in lentiviral RNF20- and/or SREBP1c-overexpressing ACHN cells. (D) RNF20- and/or SREBP1c-overexpressing ACHN ccRCC cells were subjected to qRT-PCR. (E) ACHN ccRCC cells were transduced with RNF20 and/or SREBP1c lentivirus, and their ability to form colonies was determined by crystal violet staining. (F) ACHN ccRCC cells were transduced with RNF20 and/or SREBP1c lentivirus, and cell proliferation was monitored by the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. (G) RNF20 and/or SREBP1 was suppressed in ACHN ccRCC cells using siRNAs, and cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting. (H) Intracellular triglyceride contents were measured in RNF20- and/or SREBP1-suppressing ACHN cells. (I) ACHN ccRCC cells were transfected with siRNF20 and/or siSREBP1, and relative cell growth rates were monitored using the CCK-8 assay. (J) ACHN ccRCC cells were transfected with siRNAs for suppression of RNF20 and/or SREBP1, and relative mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR. The data shown are representative results for at least three independent experiments. Data presented are the means ± SD. Significance versus negative control: #, P < 0.05; ##, P < 0.01; ###, P < 0.001. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.