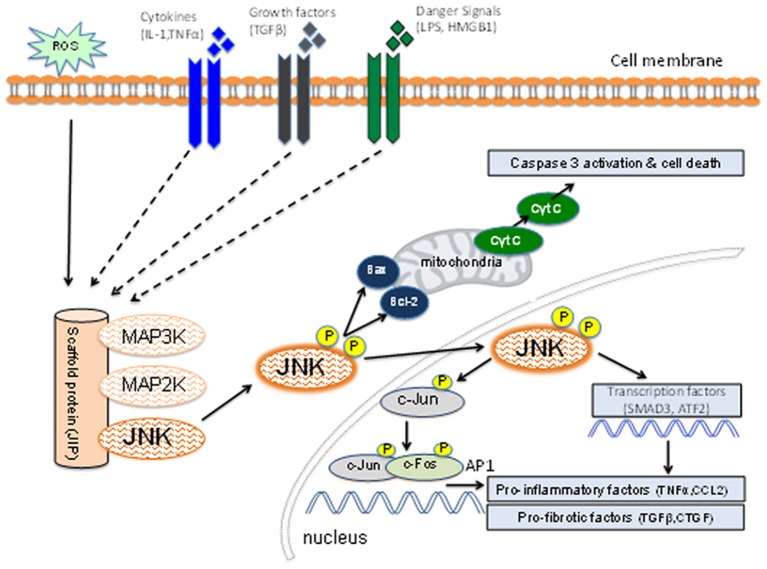
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the JNK signaling pathway. Inflammatory cytokines, danger-associated molecules pattern ligands (alarmins), and pro-fibrotic growth factors can induce activation of members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAP3K) family. Other factors such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) and osmotic stress can also lead to MAP3K activation. Individual members of the MAP3K and MAP2K families plus JNK are held in close proximity by the scaffold protein (JNK-interacting protein-1) which facilitates a rapid series of phosphorylation reactions leading to phosphorylation of the activation site of JNK. The activated JNK then dissociates from this complex and can promote mitochondria-dependent apoptosis through B cell lymphoma (Bcl-2) and Bcl-2 associated x-protein (Bax). Active JNK can promote transcription of genes involved in the inflammatory and fibrotic responses through phosphorylation of c-Jun [to promote activator protein-1 (AP-1) function], SMAD3 and ATF2. JNK activation can promote cell death, inflammation and fibrosis.