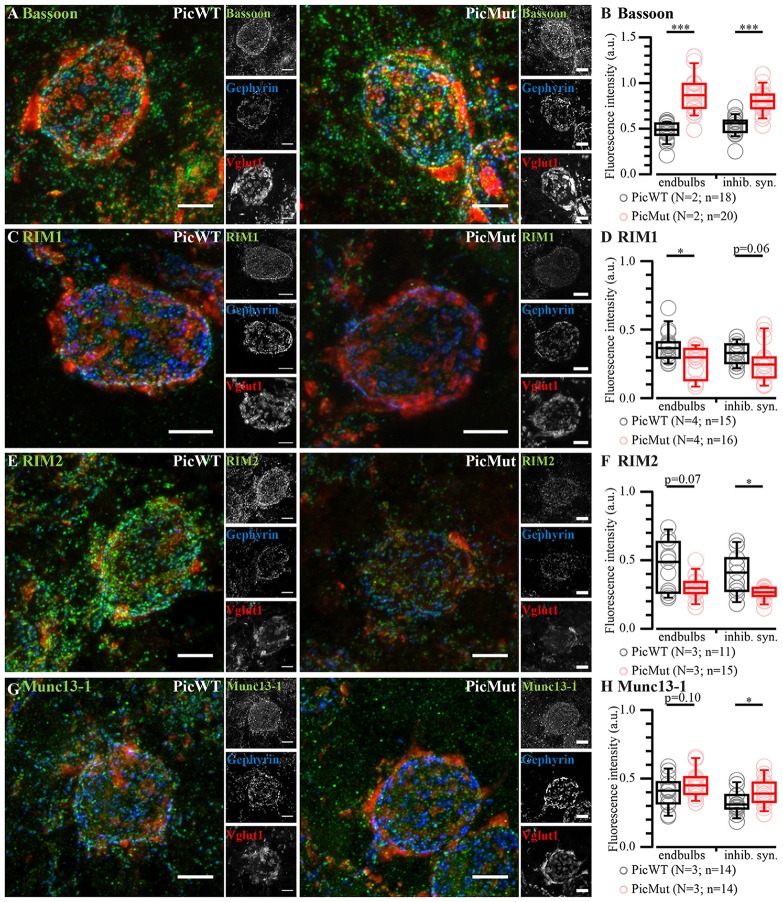
Figure 4.
Altered molecular composition at aVCN synapses in PicMut. (A,C,E,G) Maximal projection of confocal image stacks of BCs in PicWT (left) and PicMut (right). Slices were immunolabeled for different CAZ proteins: Bassoon (A), RIM1 (C), RIM2 (E) and Munc13-1 (G) and co-stained for Vglut1 (excitatory synapses) and Gephyrin (inhibitory synapses). (B,D,F,H) Quantification of fluorescence intensity of CAZ proteins at endbulbs and (inhibitory synapses) of BCs: Bassoon fluorescence intensity (B) was significantly increased at AZs of both endbulbs and inhibitory synapses in the mutant. RIM1 (D) fluorescence intensity was significantly lower at the endbulb AZs in mutant but only tended to be lower at inhibitory AZs. RIM2 (F) fluorescence intensity tended to be reduced at all AZs, but this reached significance only at inhibitory AZs. Munc13-1 (H) fluorescence intensity tended to be slightly increased, which reached significance only at inhibitory AZs. Data information: N, number of animals; n, number of BCs. All scale bars −5 μm. All data presented as box and whisker plots (median, lower/upper quartiles, 10–90th percentiles). Statistical significance between groups was determined by either unpaired Student’s t-test (in case of normally distributed data with comparable variances between the groups) or Wilcoxon rank sum test (when data distribution did not satisfy the criteria). Normality of distribution was tested with Jarque-Bera test and variances were compared with F-test. *p-value < 0.05, ***p-value < 0.001. PicWT and PicMut samples were strictly treated in parallel and images were acquired in parallel, using same laser power, gain and microscope settings.