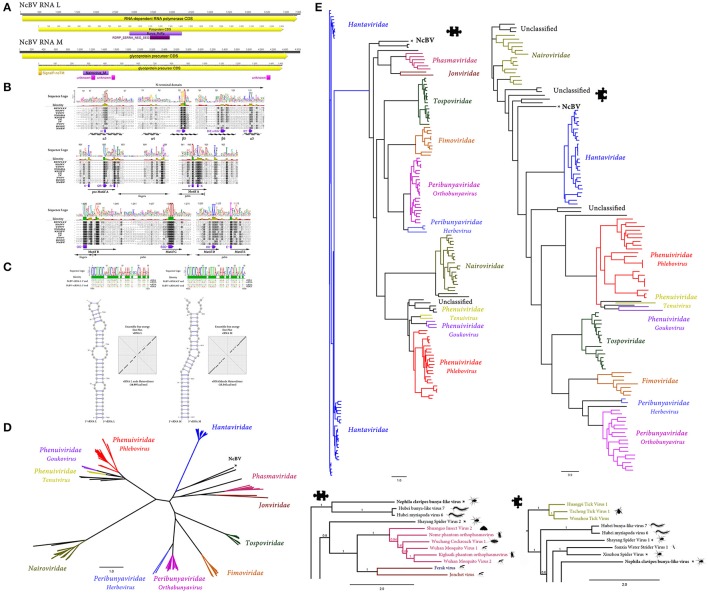
Figure 3.
Nephila clavipes Bunyavirales like virus (A) Genome graphs depicting genome segments and predicted gene products of N. clavipes bunya-like virus (NcBV). Pfam, PROSITE, GENE3D, and SignalP predicted domains (E-value ≤ 1e-5) are shown in purple, Bordeaux, pink and orange, respectively. Predicted domain data is available in Supplementary Table 9. (B) MAFFT alignment of L replicase protein of NcBV and type members of Bunyavirales families. Hantaan orthohantavirus (Hantaviridae–HANV), European mountain ash ringspot-associated emaravirus (Fimoviridae–EMARA), Ferak orthoferavirus (Feraviridae–FV), Jonchet orthojonvirus (Jonviridae–JV), Dugbe orthonairovirus (Nairoviridae–DONV), Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus (Peribunyaviridae–BUNYAV), Kigluaik phantom orthophasmavirus (Phasmaviridae–KPOPV), Rift Valley fever phlebovirus (Phenuiviridae–FVFV), Tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus (Tospoviridae–TSWV). (C) Sequence alignment of vRNA and vcRNA termini of NcBV genome segments L and G. Secondary structure prediction of RNA base pairing between the genome segment ends of NcBV, forming a double-stranded “panhandle” structure. NcBV L and G vRNAs present highly complementary genome termini, extending over 30 nt. Ensemble free energy of G and L vRNAs termini heterodimer expressed as dot plot. (D) Maximum likelihood unrooted branched phylogenetic tree based in MAFFT alignments of predicted L replicase protein of Nephila clavipes bunya-like virus (black stars) and related viruses. Family of viruses of the Bunyavirales order are indicated by colors. Scale bar represents substitutions per site. (E) Rooted layout of the preceding phylogenetic tree. Magnifications of relevant regions of the tree are presented below and indicated by puzzle pieces. Reported hosts of viruses are represented by silhouettes. Branch labels represent FastTree support values. Complete tree showing tip species, host and virus assigned taxonomy labels are available as (Supplementary Figures 7–9).