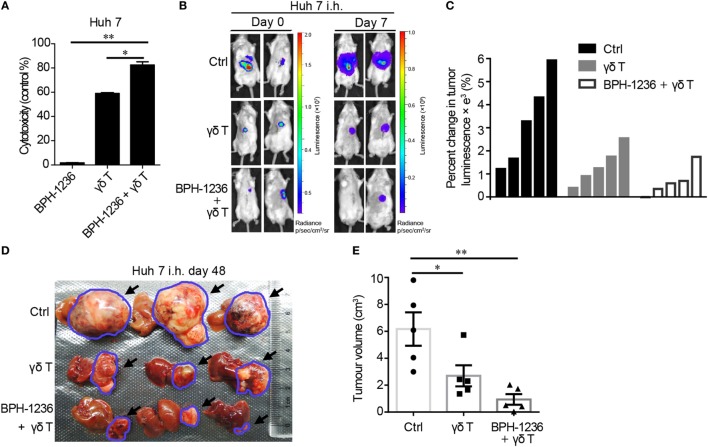
Figure 8.
Adoptively transferred Vγ9Vδ2 T cells and BPH-1236 combine to kill hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumors in an orthotopic Rag2−/−γc−/− mouse model. (A) Cytotoxicity (lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay) of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells against human Huh 7 cells pretreated with BPH-1236. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three replicates from a representative experiment of three independent experiments. (B) Representative bioluminescence images showing volume of orthotopic Huh 7/Luc tumors in Rag2−/−γc−/− mice on day 0 (before treatment) and day 7 (7 days after treatment); n = 5 per group. (C) Percent changes in tumor volume (luminescence value) in (B) from day 0 (baseline) to day 7 are shown for each mouse (n = 5 per group) as a waterfall plot (in comparison with control (Ctrl), γδ T cells: P < 0.05; BPH-1236 + γδ T cells: P < 0.05; two-tailed Student’s t-tests). (D) Representative liver/tumor images from each group (n = 5 per group) at day 48 after tumor transplantation (The treatments were given at day 7 as well as day 15 after Huh 7/Luc cells transplantation). Black arrows and blue circles highlight the tumors in liver. (E) Tumor volume in (D) at day 48 after tumor transplantation. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.