Figure 4.
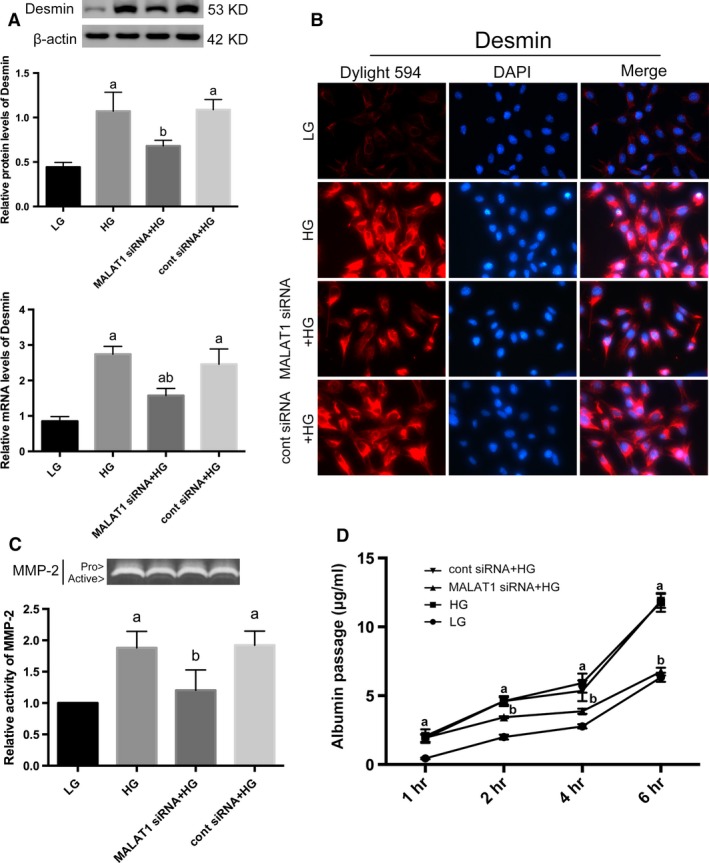
Determination of injury markers of podocytes. (A) By Western blot and real‐time PCR analysis, we showed desmin expression was induced by HG stimulation on both protein and mRNA levels, whereas diminished by MALAT1 siRNA transfection. Podocytes under culture of LG or transfected with cont siRNA were the controls. Values denote the mean ± S.D.; aP < 0.01 versus LG,bP < 0.05 versus HG. (B) Immunofluorescence further confirmed the cellular damage and restoration of podocytes. Desmin was faintly stained under LG conditions but highly expressed in a paranuclear pattern after HG incubation for 48 hrs; MALAT1 siRNA transfection prevented and reduced staining of desmin. Magnification 400 × . (C) Gelatin zymography demonstrated a hyperactivity of MMP‐2 after HG treatment for 48 hrs, which was ameliorated by MALAT1 siRNA transfection. Podocytes under culture of LG or transfected with cont siRNA were the controls. Values denote the mean ± S.D.; aP < 0.01 versus LG,bP < 0.01 versus HG. (D) Graphic presentation of the albumin influx across podocyte monolayer. Podocyte monolayer on collagen I‐coated transwell filters was incubated with LG or HG for 48 hrs. HG resulted in impaired filtration barrier function of podocyte monolayer, which was rectified by MALAT1 siRNA transfection. Podocytes under culture of LG or transfected with cont siRNA were the controls. Values denote the mean ± S.D.; aP < 0.01 versus LG,bP < 0.01 versus HG.
