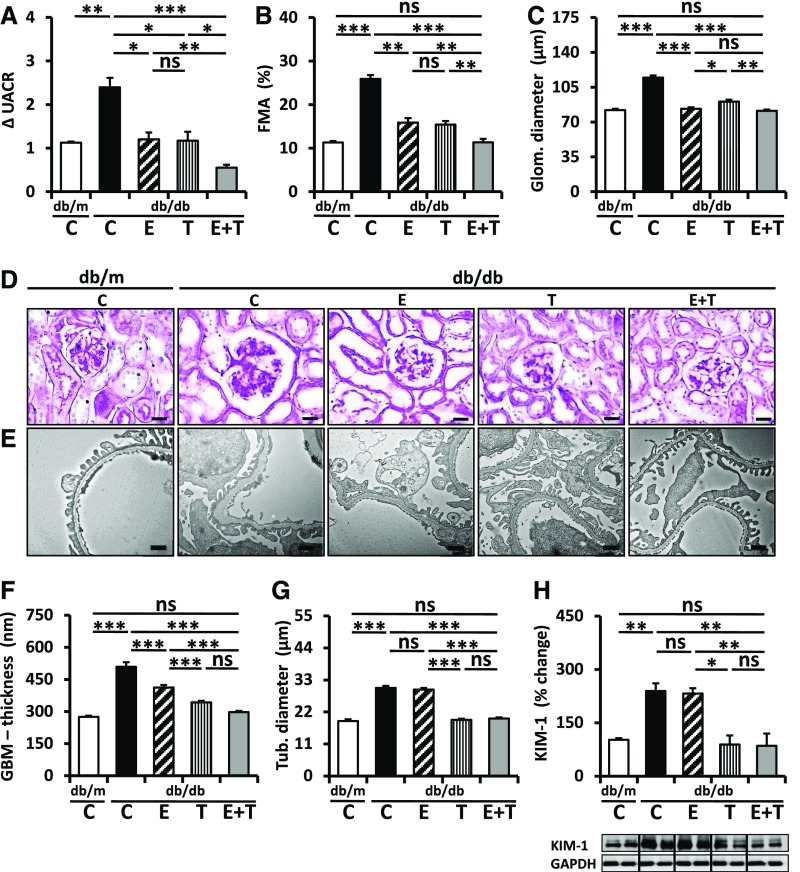
Figure 3.
TUDCA provides add-on protection on top of enalapril in db/db mice. (A) Combined treatment with enalapril and TUDCA (E+T) over 6 weeks reduces the increase of albuminuria (ΔUACR, fold change of the urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio) in db/db mice more efficaciously than treatment with enalapril (E) or TUDCA (T) alone. (B–F) Enalapril (E), TUDCA (T), and the combination of enalapril and TUDCA (E+T) reduce glomerular damage, as reflected by extracellular matrix accumulation (fractional mesangial area [FMA]) (B and D), glomerular diameter (C and D), or glomerular basement membrane (GBM) thickness (E and F) to an overall comparable extent. Representative PAS-stained histologic sections (D) and transmission electron microscope (E) images. (G and H) TUDCA (T), but not enalapril (E), reduces tubular damage, as reflected by tubular diameter (G, see also D) and KIM-1 expression (H). Bar graphs reflecting mean±SEM (A–C and F–H) of at least six mice in each group (number of mice per group: C, db/m, 6; C, db/db, 10; E, 6; T, 8; E+T, 6); representative immunoblots (H, bottom); scale bar, 20 μm (D) or 1 µm (E); *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 (one-way ANOVA).