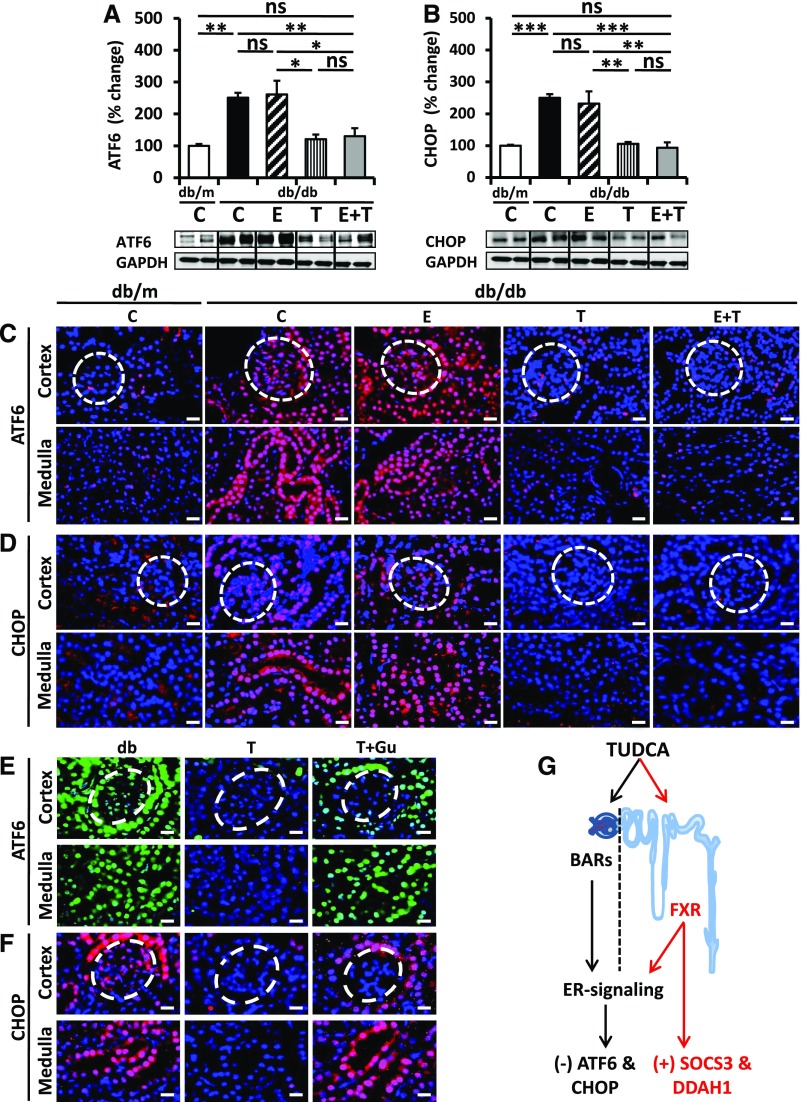
Figure 4.
TUDCA but not enalapril ameliorates ER stress in tubular cells. (A and B) TUCDA but not enalapril reduces the ER stress markers ATF6 (A) and CHOP (B) in renal extracts. The combined treatment of enalapril plus TUDCA (E+T) has no additive effect on ER stress markers. Bar graphs reflecting mean±SEM (A and B, top) of at least six mice in each group (number of mice per group: C, db/m, 6; C, db/db, 10; E, 6; T, 8; E+T, 6); representative immunoblots (A and B, bottom); *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 (one-way ANOVA). (C and D) Immunofluorescence analyses of ATF6 (C) and CHOP (D) expression in outer renal cortex (top, glomeruli indicated by the white dashed circles) and in inner renal tissue (medulla, bottom) in control decibels per meter (C) and diabetic (db/db) without treatment (C), enalapril (E), TUDCA (T), or enalapril plus TUDCA (E+T) treatment; scale bar, 20 μm (C and D). (E and F) Immunofluorescence analyses of ATF6 (E) and CHOP (F) expression in outer renal cortex (top, glomeruli indicated by the white dashed circles) and in inner renal tissue (medulla, bottom) in control diabetic (db/db) mice without treatment (db), TUDCA (T), or concomitant treatment with Z-guggulsterone (T+Gu), scale bar, 20 μm (E and F). (G) Proposed model showing the tubular specific effect of TUDCA via FXR agonism. TUDCA ameliorates ER stress in the glomerular and tubular compartment. Within the tubular compartment alleviation of ER stress depends on FXR, whereas other bile acid receptors (BARs) in the glomerular compartment remain to be identified. TUDCA may provide additional tubular protective effects via FXR-dependent regulation of SOCS3, DDAH1, or other genes.