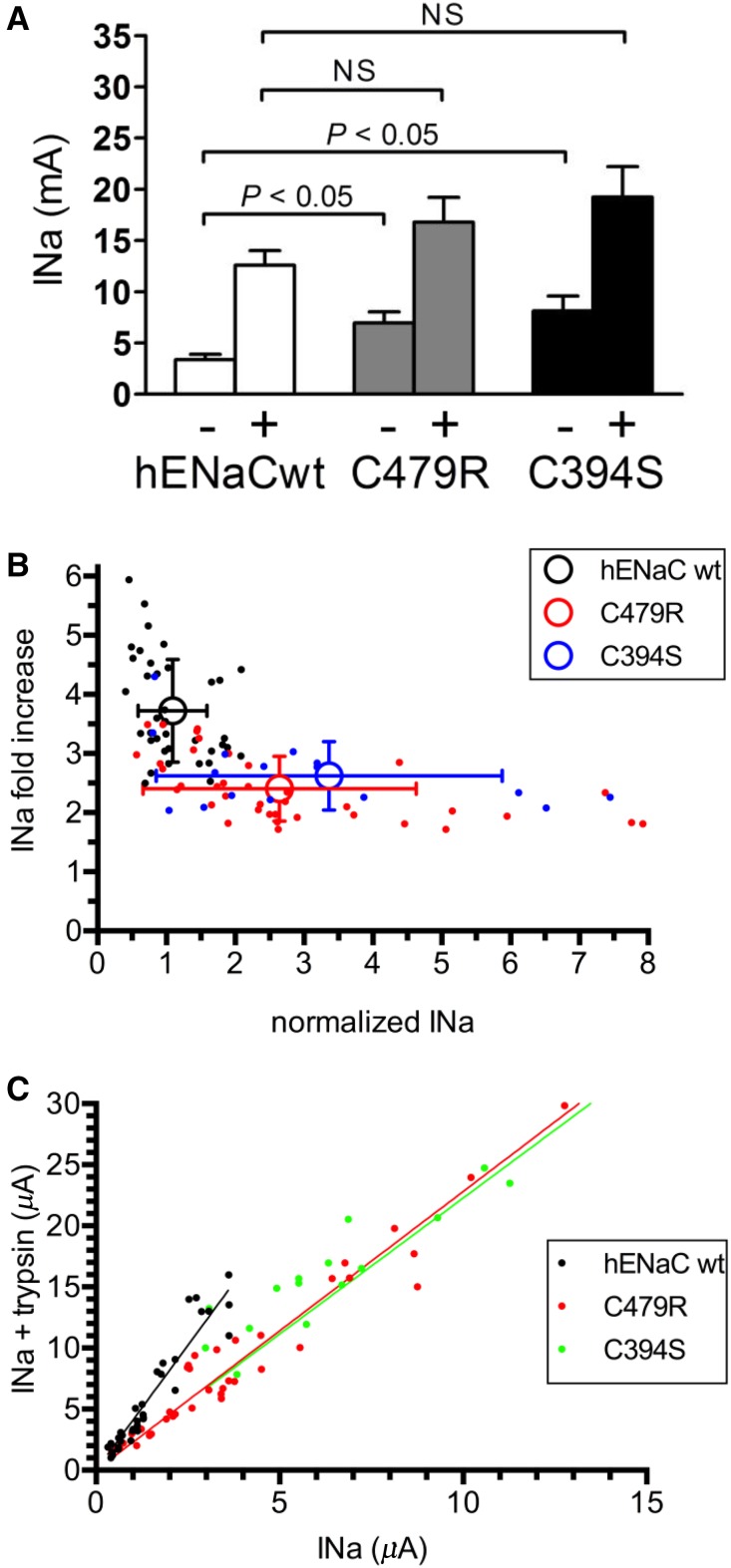
Figure 5.
Lower trypsin sensitivity of C479R and C394S than wild type αENaC suggests higher intrinsic channel activity. (A) Amiloride-sensitive current (microampere) of hENaC wild-type (wt; n=17), hαENaC C479R (n=17), and hαENaC C394S (n=18) in the absence (−) or presence (+) of trypsin. The magnitude of the currents in the absence of trypsin was significantly higher for C479R and C394S compared with wt (P<0.01 by one-way ANOVA), whereas the currents in oocytes expressing the mutant forms were no longer significantly higher after trypsin treatment. (B) Relationship between baseline INa in the absence of trypsin and fold increase in INa after the addition of trypsin in wt and mutant human ENaC (C479R and C394S). Current values for a single oocyte (filled symbols) and means±SD (open symbols) are shown (P<0.01 by ANOVA). (C) Correlation between current INa (microampere) values in the absence and presence of trypsin. Linear regression analysis gives the following best fit values for the slopes hαwt (4.08; 95% confidence interval, 3.82 to 4.35), hαC479R (2.28; 95% confidence interval, 2.14 to 2.42), and hαC394S (2.23; 95% confidence interval, 2.03 to 2.42). Supplemental Figure 3 shows original traces. INa, Na+ current.