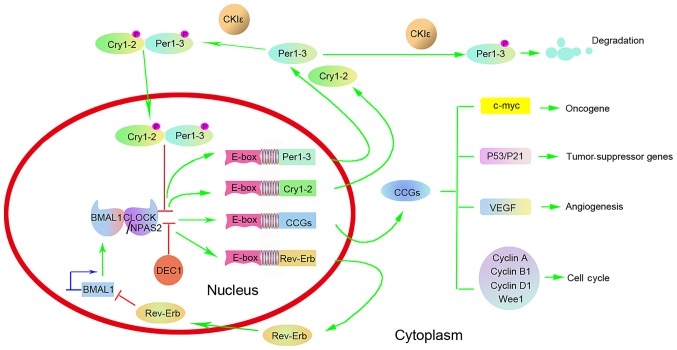
Figure 1.
Representation of the circadian clock network. CLOCK or NPAS2 combines with BMAL1 to form a core CLOCK/BMAL1 or NPAS2/BMAL1 transcriptional complex, which subsequently activates the transcription of Per1-3 and Cry1-2 via E-box elements on their promoters. DEC1 can compete with CLOCK/BMAL1 or NPAS2/BMAL1 heterodimers for E-box binding and therefore inhibit CLOCK/BMAL1-mediated transactivation. The coding products, the Per1-3 and Cry1-2 proteins, form a multimeric complex, translocate from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and inhibit CLOCK/BMAL1-mediated transcription. Degradation of Per1-3 and Cry1-2 proteins prompts a new circadian cycle whereby CLOCK/BMAL1 transcription is reinitiated. The CLOCK/BMAL1 heterodimer also activates the transcription of the orphan nuclear receptor Rev-Erb gene. The protein encoded by the Rev-Erb gene can combine with the BMAL1 promoter and block its transcription. Besides transcriptional regulation, post-translational modifications are also involved in the modulation of circadian proteins. CKIε can phosphorylate Per1-3 and Cry1-2 proteins, and enable Per1-3 and Cry1-2 proteins to be translocated from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. In addition, CKIε-mediated phosphorylation can also destabilize Per1-3 proteins. Finally, the CLOCK/BMAL1 complex regulates the expression of CCGs, including oncogenes (c-myc), tumor-suppressor genes (P53 and P21), genes involved in the regulation of the cell cycle (cyclins A, B1 and D1, and WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase) and VEGF. These target genes regulated by the biological clock genes are involved in DNA repair, cell proliferation and apoptosis. Therefore, circadian clock disorders may lead to uncontrolled cell growth and malignant transformation. CLOCK, circadian locomotor output cycles kaput; NPAS2, neuronal Per-Arnt-Sim domain-containing protein 2; BMAL1, brain and muscle arylhydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like 1; Per, period; Cry, cryptochrome; DEC, differentiated embryo-chondrocyte expressed gene; CKIε, casein kinase Iε; CCG, circadian-clock-controlled gene; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.