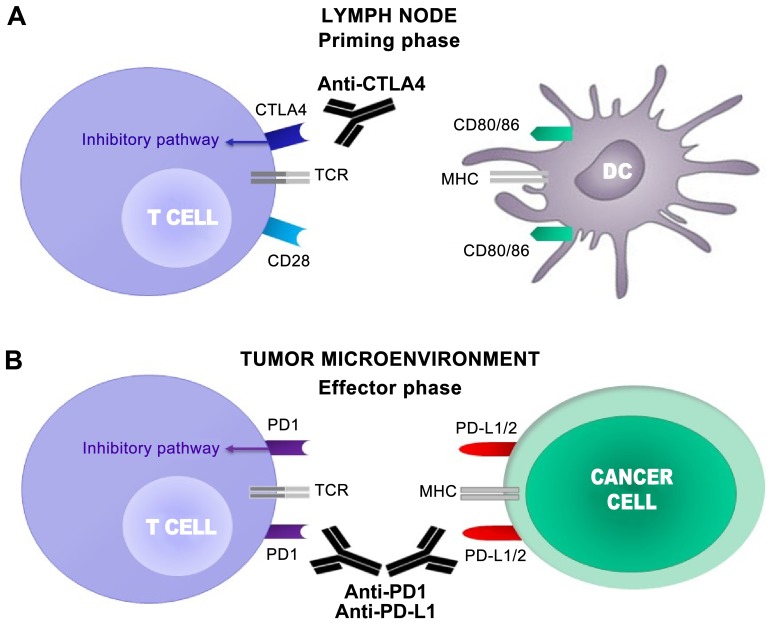
Figure 1.
CTLA4 and PD1 regulate different stages of T cell response. (A) T cell activation requires two complementary signals: The interaction between the TCR and peptide-MHC complex must be associated with a second co-stimulatory signal mediated by CD28. Conversely, the binding of CTLA4 to CD80/86 provides a control signal that suppresses ongoing T cell activation. (B) PD1 is upregulated on T cells following persistent antigen exposure. When PD1 binds to its ligand, PD-L1 or PD-L2, expressed by tumor cells, the T cell receives an inhibitory signal. Antibodies against CTLA4 or PD1/PD-L1 can activate T cells. CTLA4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; PD1, programmed cell death protein 1; TCR, T cell receptor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; CD, cluster of differentiation; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; PD-L2, programmed death ligand 2; DC, dendritic cell.