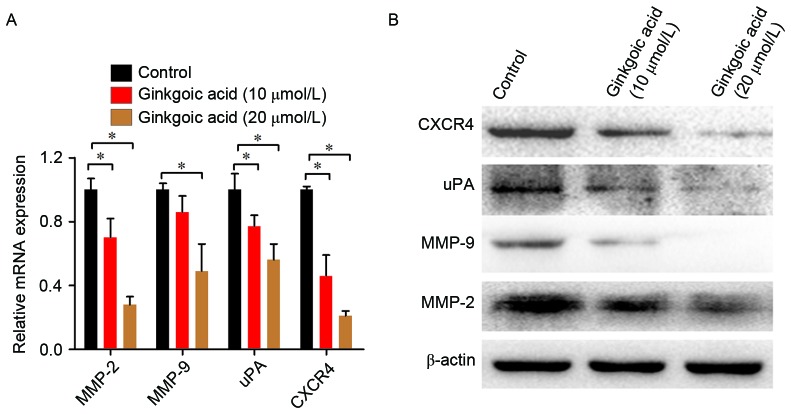
Figure 3.
Ginkgolic acid suppresses the expression of invasion-associated genes and proteins. (A) SW480 cells were treated with ginkgolic acid at various concentrations (0, 10 and 20 µmol/l) for 24 h, and the mRNA levels of invasion-associated markers (MMP-2 and −9, uPA and CXCR4) were measured by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. The expression of each target gene was quantified using β-actin as a normalization control. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05. (B) The protein levels of invasion-associated markers were measured by western blotting following ginkgolic acid treatment for 48 h. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; uPA, urinary-type plasminogen activator; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor 4.