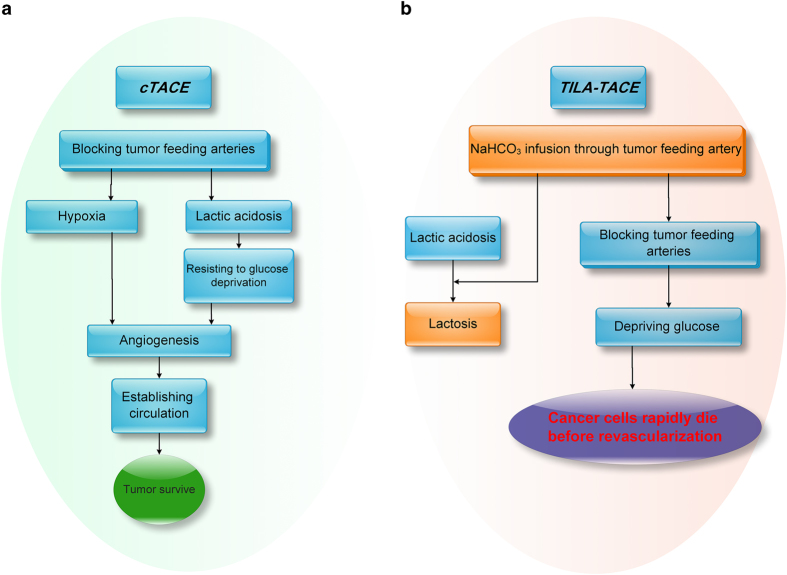
Figure 5.
The hypothetical approach to treat large HCC by targeting intratumoral lactic acidosis. (a) cTACE embolizes tumor feeding artery that blocks glucose supply but also traps lactic acidosis, which, in turn, rescues cancer cells from glucose deprivation. cTACE also creates a hypoxia condition. The lactic acidosis-rescued cancer cells under hypoxia can emit strong signal to initiate angiogenesis and ultimately reestablish circulation to support tumor. Thus, the chance for tumor survival is increased. (b) TILA-TACE is designed to test if lactic acidosis is the major factor that determines tumor cell survival after embolization. If yes, neutralizing lactic acidosis by bicarbonate would rapidly kill cancer cells and block the subsequent biological processes and significantly improve the therapeutic efficacy.