Figure 2. Change in Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS) Over the First 8 Hours After Treatment.
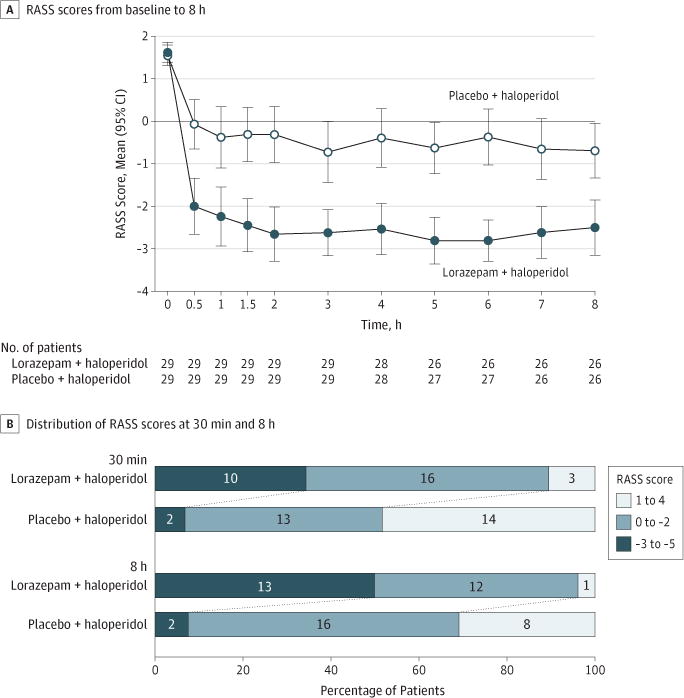
A, Time 0 indicates immediately before treatment administration. Error bars indicate 95% CIs. Both treatments were associated with significant reduction in the mean RASS score within the first 30 minutes of treatment. RASS score remained relatively stable for both groups over the 8-hour observation period. Lorazepam + haloperidol was associated with a significantly greater reduction in RASS score than placebo + haloperidol at 8 hours (P < .001, 2-sided Wilcoxon rank sum test). B, A larger proportion of patients had hyperactivity (RASS score, 1 to 4) in the placebo + haloperidol group at both 30 minutes and 8 hours (P = .001 for both time points). In contrast, a larger proportion of patients had sedation in the lorazepam group (RASS score, −3 to −5). The 2-sided Fisher exact test was used to compare the 3 categories of RASS scores between groups.
