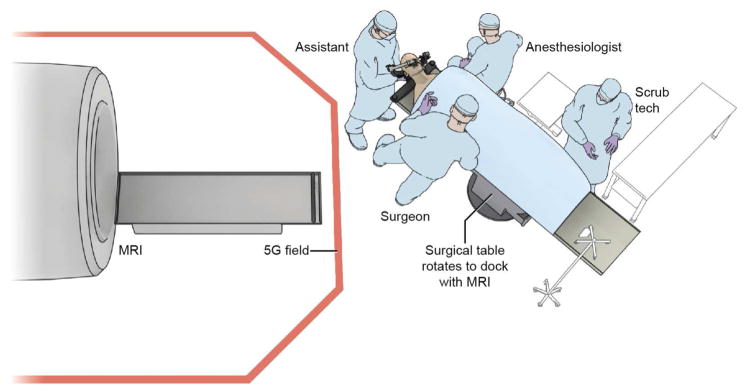
Figure 1.
The high field (1.5 Tesla) iMRI system at the Clinical Center of National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD. The initial surgical approach is performed on the surgical table as usual. An MR imaging–compatible patient reference frame (Polestar, Medtronic, Inc.) is attached to the head holder using an MR imaging–compatible, custom-designed patient reference frame holder (Integra Life Sciences Corp.). The neuronavigation system (StealthStation, Medtronic Inc.) is registered and a microscopic or endoscopic transsphenoidal approach, and initial adenoma resection is performed. For intra-operative imaging, the surgical table is rotated to dock with the iMRI. Following image acquisition, the subject is brought back outside the 5 Gauss (5G) field line for resumption of the surgical process and/or closure.