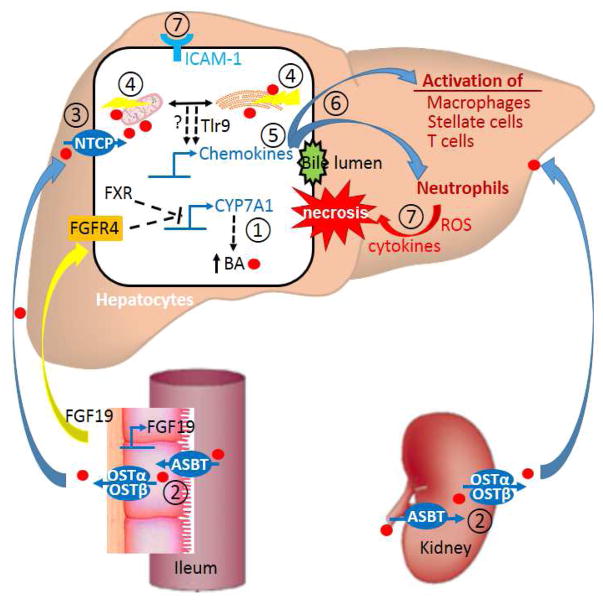
Figure 1.
A hypothetic model of bile acid induced liver injury and potential therapeutic targets for treating cholestatic disorders. The intervention sites are listed as ① repress bile acid synthesis in hepatocytes; ② block bile acid reabsorption in intestine and kidney; ③ block hepatic uptake of bile acid; ④ reduce bile acid caused mitochondrial damage and ER stress in hepatocytes; ⑤ inhibit inflammatory chemokine production; ⑥ prevent inflammatory response by antagonize cytokine receptors in immune cells; ⑦ prevent neutrophils and immune cells from attacking injured hepatocytes. An agent targeting a specific site or the combination of agents targeting multiple sites are predicted to be beneficial for patients with cholestasis.