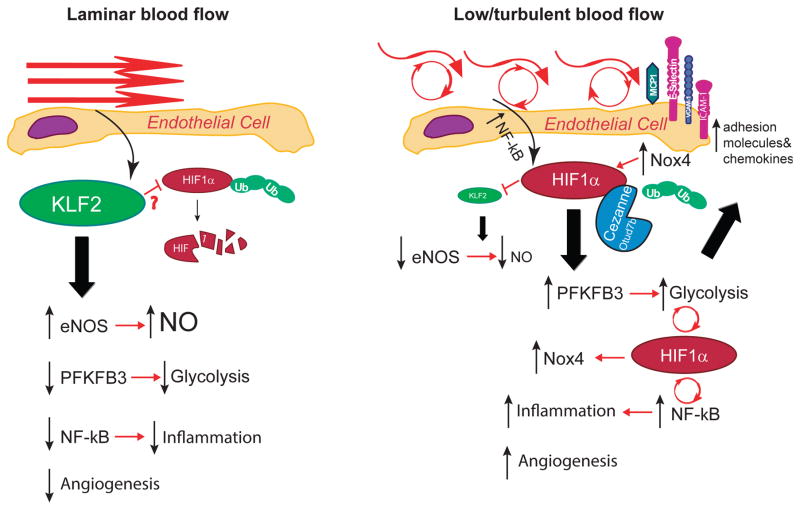
Figure 1. Mechanosensitive pathways in endothelial cells subject to (A) laminar flow or (B) disturbed flow.
Laminar shear stress upregulates KLF2 which has been shown to inhibit HIF1α by promoting its degradation and collectively these events lead to increased expression of homeostatic enzymes such as eNOS, inhibition of NF-κB and inflammation, decreased angiogenesis and suppression of key glycolytic enzymes such as PFKFB3. In contrast, turbulent flow and oscillatory shear stimulate NF-κB which induces HIF1α resulting in the loss of KLF2. HIF1α protein expression is stabilized by the upregulation of Cezanne which removes ubiquitin modifications and also by Nox4. HIF1α drives increased glycolysis, inflammatory signaling via NF-κB and expression of adhesion molecules as well as increased angiogenesis.