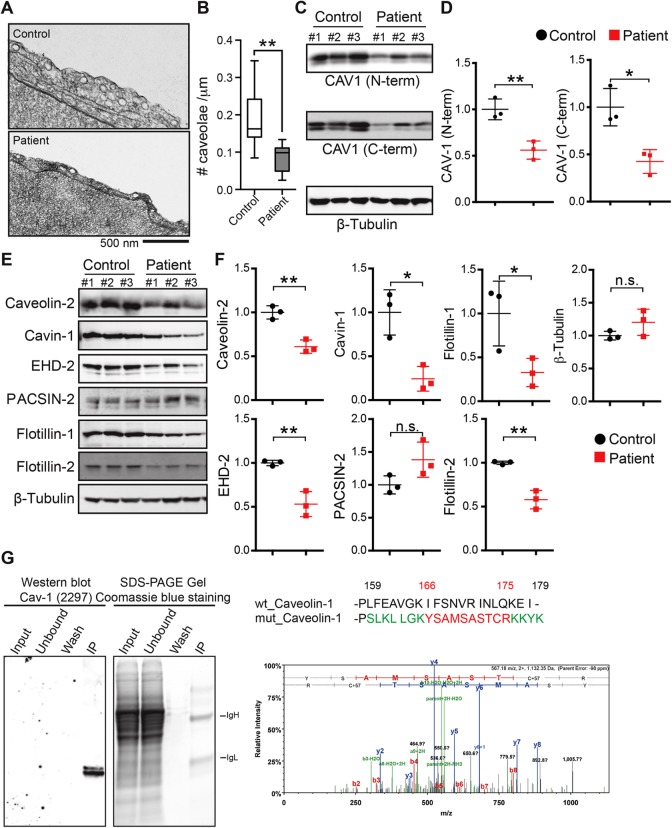
FIGURE 7:
The density of caveolae and caveolar protein levels are reduced in patient cells expressing CAV1-P158. (A) Cropped electron micrographs of control (top panel) and patient (bottom panel) skin fibroblasts. Images were acquired at 30,000× magnification. For purposes of illustration, the density of caveolae in these images is higher than the average values quantified in B. Scale bar, 500 nm. (B) Quantification of number of caveolae per micrometer of plasma membrane in patient and control fibroblasts. Caveolae were counted in 25 images each from three patients and three control cell lines in two independent experimental replicates and one experiment for one control and one patient cell line. **, p < 0.007, nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test. (C, D) Representative Western blots and densitometry analysis of CAV1 in control and patient fibroblasts as detected using N-term and C-term specific antibodies. b-Tubulin was blotted as a loading control. Densitometry data were averaged over three control and patient cell lines and the mean ± SD are indicated. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, Student’s t test. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (E, F) Representative Western blots and densitometry analysis of caveolar accessory proteins in control and patient skin fibroblasts. β-tubulin was blotted as a loading control. Densitometry data were averaged of three control and patient cell lines. n.s., not significant; *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, Student’s t test. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (G) Tandem mass spectrometry was used to determine if CAV1-P158 protein is expressed in patient fibroblasts. CAV1 protein was immunoprecipitated using CAV1 N-term from lysates of a patient fibroblast cell line, separated by SDS–PAGE, and Coomassie stained. Immunoprecipitated CAV1 was also detected in immunoblots with an anti-CAV1 mAb 2297. The region of the SDS–PAGE gel that corresponded to the position of the CAV1 band in the immunoblot was excised and analyzed by mass spectrometry. Unique peptides of the novel C-terminus of CAV1-P158 were detected in patient cells.