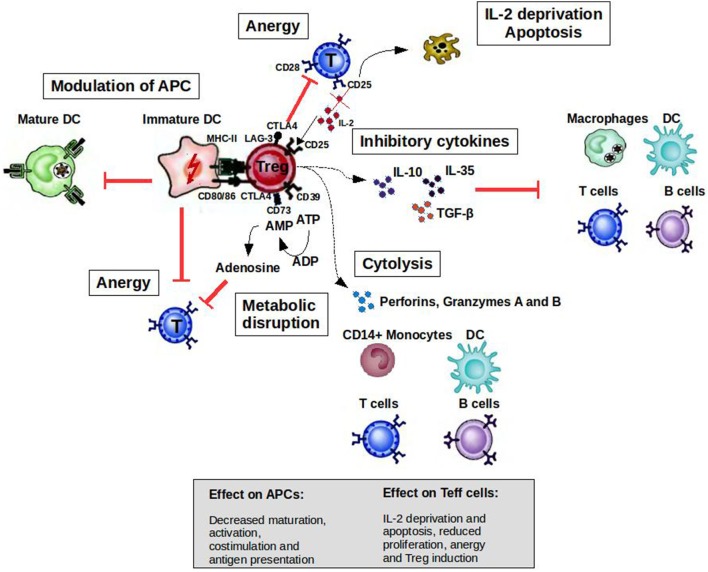
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of suppression by Treg cells to control immune responses. A broad range of molecular mechanisms contribute to the suppressive function of Tregs. Mechanisms include the following: apoptosis/cytolysis (IL-2 deprivation, granzyme A/B, perforins); antigen-presenting cell (APC) modulation (CTLA4, LAG-3); inhibitory cytokines (IL-10, IL-35, and TGF-β); and metabolic disruption (CD73/39 and ATP/adenosine mechanism). Abbreviations: CTLA4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4; DC, dendritic cell; CD, cluster of differentiation; IL, interleukin; Treg cell, regulatory T cell; LAG-3, lymphocyte activation gene 3; TGF, transforming growth factor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex.