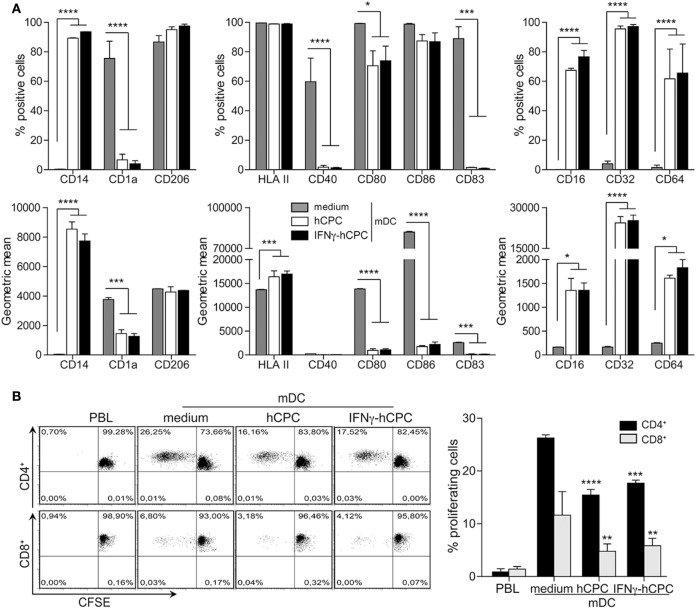
Figure 6.
Human cardiac-derived stem/progenitor cells (hCPC) confer macrophage-like profile and impair the capacity of mature DC (mDC) to induce allogeneic T cells proliferation. CD14+CD16− monocytes were differentiated into immature cells as in Figure 5 then their maturation to mDC was induced with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). (A) Expression of relevant markers (left panel), of dendritic cell maturation markers (middle panel), and of FCγR (right panel) by CD14+CD16− monocyte-derived mDC in the absence (medium) or the presence of hCPC (hCPC) or IFNγ-hCPC (IFNγ-hCPC) as determined by flow cytometry. Results are presented as the percentage of positive cells (upper panel) and geometric mean (lower panel). (B) CD14+CD16− monocyte-derived mDC in the absence (medium) or the presence of hCPC (hCPC) or IFNγ-hCPC (IFNγ-hCPC) were used to stimulate the proliferation of allogeneic carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE)-labeled peripheral blood lymphocyte (PBL) at a PBL/DC ratio of 5:1 as described under Section “Materials and Methods.” The percentage of CD4+ and CD8+ proliferating T-cells was determined by flow cytometry as described in Figure 4. Results are presented as representative dot plots of proliferating cells (left panel). Histograms (right panel) represent % of proliferating cells compared to medium. Data on the graphs represent the mean ± SEM from four independent experiments conducted with peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) isolated from four different donors against the same hCPC and are representative of data obtained with two other hCPC from different donors. Each data point represents the mean of experimental triplicates. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.