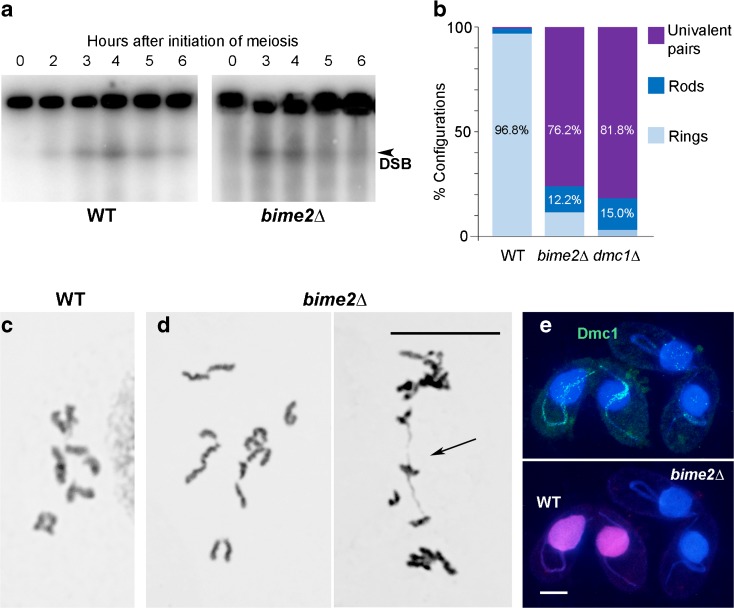
Fig. 2.
Deletion of BIME2 prevents chromosome pairing and inhibits Dmc1 chromatin localization. a Southern hybridization of DSB-dependent chromosome fragments separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis using a probe specific to the germline nucleus. DSB formation is similar in wild-type and bime2Δ cells. b Ring bivalents are mainly formed in the wild type, whereas univalents and rare bivalents are formed in bime2Δ and dmc1Δ meiosis. In wild type and bime2Δ, 500 configurations (bivalents or pairs of univalents) were counted; in dmc1Δ, 400 configurations were counted. c, d Examples of Giemsa-stained diakinesis-metaphase I wild-type (c) and bime2Δ (d) nuclei (arrow indicates a rod bivalent). e Chromatin-associated Dmc1 foci are present in elongated prophase nuclei in wild-type mating cells (distinguished by mCherry-tagged histone—magenta), but foci numbers are greatly reduced in bime2Δ mating cells. (Foci in somatic nuclei represent Rad51, which is also recognized by the anti-Dmc1 antibody). Scale bars: 10 μm