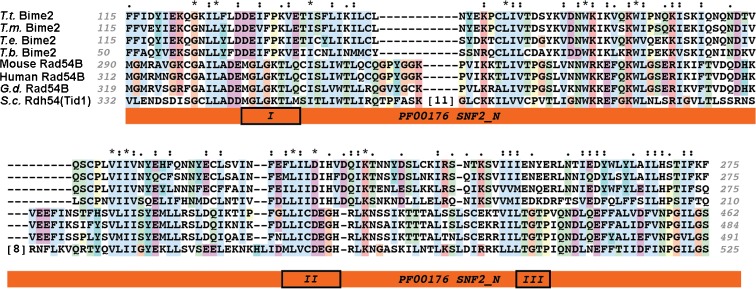
Fig. 4.
Multiple partial sequence alignment showing the region of the highest sequence similarity between Tetrahymena thermophila (T.t.) Bime2 proteins and representatives of the Rad54B family: mouse, human and chicken (Gallus domesticus (G.d.)) Rad54B and budding yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S.c.)) Rdh54/Tid1. The aligned Bime2 sequence segment was selected to include the region with significant similarity to the PANTHER family Rad54B/PTHR10799:SF918 (HMMscore versus PANTHER v11.1—E = 3.7e-09) and Pfam family PF00176/SNF2_N. Characteristic helicase sequence motifs, Motifs I (Walker A), II (DExx), and III, reported to form the primary ATP binding site in the active site cleft (Dürr et al. 2005) are marked, but appear not to be functionally conserved in Bime2. Bime2 has clear homologs only in other Tetrahymena species (T. malaccensis (T.m.), T. elliotti (T.e.), and T. borealis (T.b.)). The alignment was generated using MUSCLE v3.8.31 (Edgar 2004) and visualized using Clustalx v2.1 (Thompson et al. 1997)