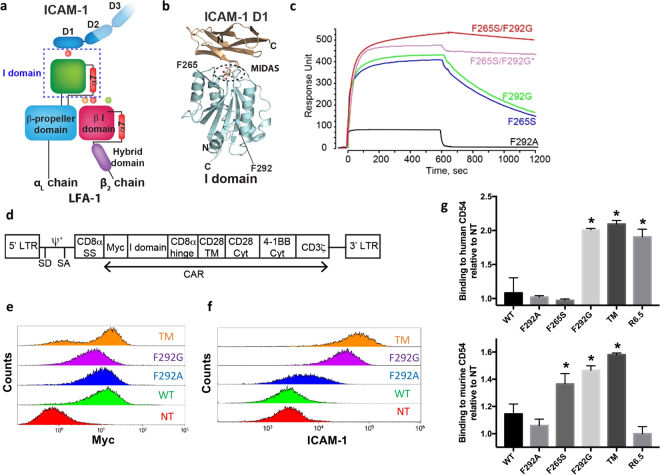
Figure 1.
Construction of ICAM-1 specific CARs with step-wise, 106-fold variations in affinity. (a) Schematic of LFA-1 in complex with ICAM-1. α and β chains, and modular domains of LFA-1 integrin are labeled. I domain of α chain is denoted with a dotted box. Metal ions necessary for LFA-1 and ICAM-1 interaction are shown in circles. (b) Structural model of LFA-1 I domain and the N-terminal domain of ICAM-1 (D1) are drawn in ribbon diagram. N and C-termini, and mutational hot spots are indicated. (c) SPR sensogram of I domain variants binding to immobilized human ICAM-1, except F265S/F292G*, which was flowed over murine ICAM-1 (adapted from Fig. 2 of Jin et al.27, and Fig. 1 of Wong et al.28). (d) A schematic of the lentivirus vector encoding I domain CAR. LTR = long terminal repeat; SD = splice donor; SA = splice acceptor; ψ+ = packaging signal; SS = signal sequence; TM = transmembrane; Cyt = cytosolic domain. (e) Anti-Myc antibody binding to Jurkat T cells transduced with Myc-tagged CARs (TM, F292G, F292A, and WT I domain). NT = non-transduced. (f) Recombinant ICAM-1-Fc binding to CARs expressed in HEK 293 T cells. (g) V-bottom adhesion assay measuring relative binding affinities between I domain CARs expressed in Jurkat T cells and soluble human (top) and murine (bottom) ICAM-1 (CD54) coated surfaces. n = 3; p < 0.01 for * vs. NT by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.