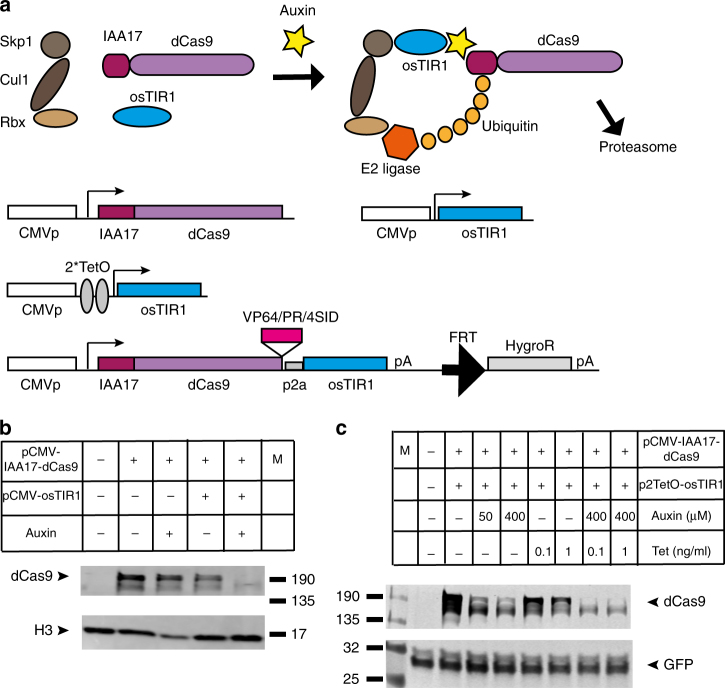
Fig. 1.
Small molecule inducible degradation control of dCas9 using the Auxin inducible degron. a Schematic overview of the AID-dCas9 system. The IAA17 peptide, which confers sensitivity to degradation upon addition of the plant hormone auxin, is fused to the N-terminus of dCas9. The cullin/skp/rbx components are present in mammalian cells, but auxiliary protein TIR1 has to be externally supplied. Upon addition of auxin a complex is formed with E2 ligase, resulting in poly-ubiquination and proteasomal degradation. IAA17-dCas9 and osTIR1 can be expressed from separate plasmids, allowing independent tetracyclin-inducible control of osTIR1 expression, or from a single combined construct suitable for Flp-mediated integration into FRT containing genomic insertion platforms. Effector domains of interest (e.g., VP64) can be fused to the C-terminus of AID-dCas9. b The IAA17 degron tagged dCas9 fusion protein is sensitive to degradation upon addition of auxin only in the presence of osTIR1. Western blot of HEK293FT cells transfected with the constructs shown in the table in the presence or absence of added auxin (400 μM) and probed with Cas9 antibody. Histone H3 antibody was used as loading control c Placing osTIR1 under control of a Tetracyclin (Tet)-inducible promoter results in degradation of IAA17-dCas9 only in the presence of both auxin and tetracyclin, effectively creating an AND or NAND gate depending on the C-terminal effector domain attached to dCas9. HEK293FT cells were transfected with pCMV-IAA17-dCas9 and pCMV-2TetO-osTIR1 and tetracycline or auxin were added as indicated in the table. A control GFP expression plasmid was co-transfected. Samples were probed on Western blot with Cas9 antibody. GFP antibody was used as loading control