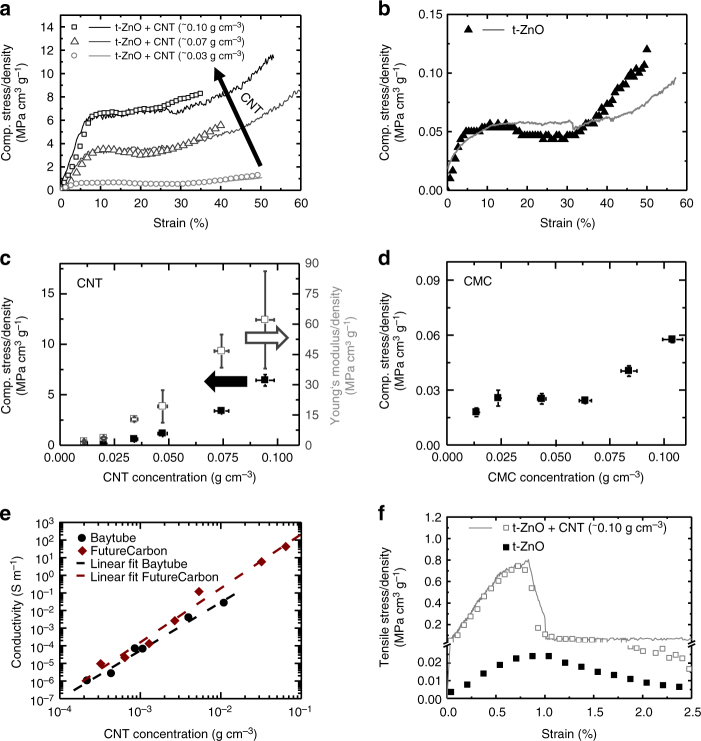
Fig. 2.
Mechanical and electrical properties of the CNTT/t-ZnO composite structure. a Compressive stress–strain curves for CNTT/t-ZnO networks containing different amounts of CNT normalized to the density of each structure (solid curves represents the corresponding results from FEM); b Compressive stress–strain curves for the pure t-ZnO network normalized to density (solid curve represents the corresponding FEM result); c Compressive strength and Young’s modulus (normalized with respect to density) vs. CNT concentration (error bars are s.d.); d Compressive strength (normalized with respect to density) vs. cellulose (CMC) concentration (stabilizing agent in the CNT dispersion) (error bars are s.d.); e Conductivity as a function of carbon nanotube concentration for two different CNT dispersions (CarboDis TN (Future Carbon), and Baytubes DW 55 CM (Bayer MaterialScience)); f Stress–strain curves under tensile loading for the pure ceramic network and for a network containing 0.1 g cm−3 carbon nanotubes (values are corrected by the density of the structures; solid curves represent the corresponding results from FEM). Please note that the template density was set to 0.3 g cm−3 for all mechanical and electrical measurements shown