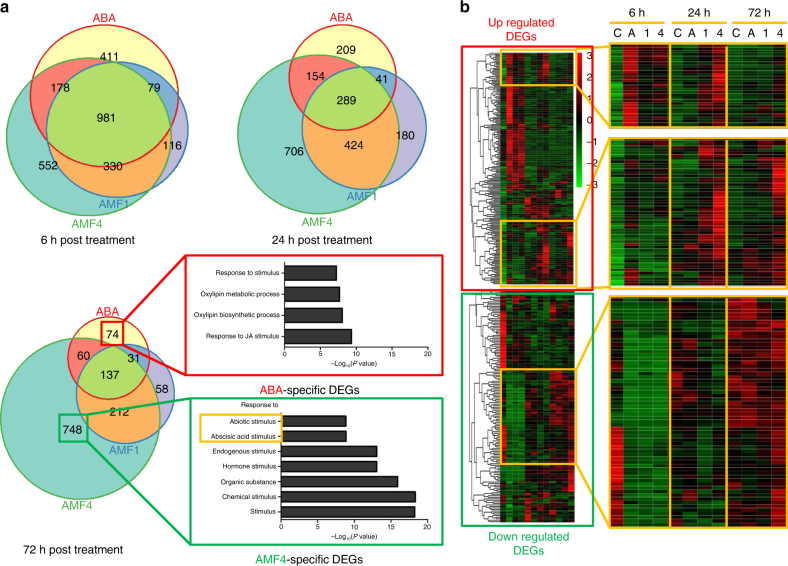
Fig. 4.
AMFs regulate ABA-responsive genes in Arabidopsis plants. Col-0 plants are sprayed with 10 μM (+)-ABA (ABA or A), AMF1β (AMF1 or 1), or AMF4 (AMF4 or 4) are sampled 6, 24, and 72 h post treatment, and DMSO (DMSO or C) is used as the control. Gene expression profiles are based on RNA-seq results. a Overlap of ABA- and AMFs-induced DEGs. AMF1β or AMF4 induce highly correlated responses at the transcript level compared with ABA. Ontology analysis of ABA- or AMF4-specific DEGs shows that some ABA- or abiotic stress-related processes are still among the most enriched biological processes (based on their P values) at 3 days after AMF4 treatment but not at 3 days after ABA treatment. b Heat map of ABA- or abiotic stress-related DEGs in Col-0 plants. DEGs are clustered based on expression profiles. Each row contains an ABA- or abiotic stress-related DEG based on gene ontology analysis. Each column represents a chemical-time combination. The DEGs showing divergent time-course response to ABA or AMFs are highlighted. The color in each cell indicates its relative expression level compared to the mean expression level in all samples of the same row according to the color bar, with red and green representing upregulated and downregulated genes, respectively