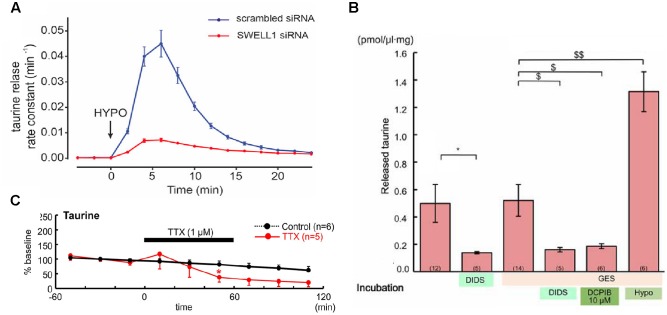
FIGURE 1.
Taurine release pathways. (A) The taurine release from HeLa cells after hypoosmotic stimulation was massively attenuated if expression of the volume-regulated anion channel SWELL1 was suppressed (with permission from Qiu et al., 2014). (B) The taurine release from embryonic neocortical slices loaded with 10 mM taurine was not affected by the TauT inhibitor GES, could be blocked the unspecific anion channel blocker DIDS or by DCPIB, a selective blocker of volume-regulated anion channels, and was stimulated by hypoosmotic stimulation (hypo), suggesting that taurine efflux was mainly mediated by volume-regulated anion channels (∗ and $ represent P < 0.05, $$ indicate P < 0.01, with permission from Furukawa et al., 2014). (C) Suppression of electrical activity attenuated the spontaneous taurine release from tangential slices of early postnatal rat neocortex, suggesting the existence of a constitutive, activity-dependent taurine release (modified with permission from Qian et al., 2014).