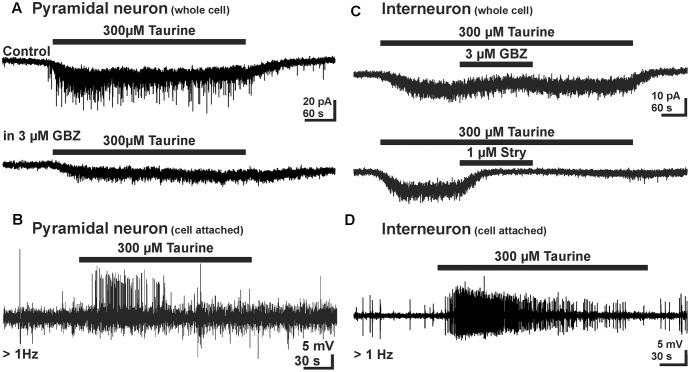
FIGURE 4.
Effect of taurine on GABAergic networks in early postnatal mouse neocortex. (A) In pyramidal neurons taurine induced a tonic inward current and increased the frequency of GBZ-sensitive GABAergic PSCs. (B) Cell-attached recordings demonstrating that GABAergic PSCs enhance action potential frequency, suggesting that the taurine-induced GABAergic PSCs are excitatory. (C) In GABAergic interneurons taurine induced an inward-current that was relatively insensitive to GBZ, but suppressed by strychnine, indicating that taurine acts mainly via glycine receptors in this cell type. (D) Cell-attached recordings from GABAergic interneurons demonstrate that the taurine-induced inward current enhances action potential frequency, suggesting that the taurine is an excitatory neuromodulator in immature interneurons (with permission from Sava et al., 2014).