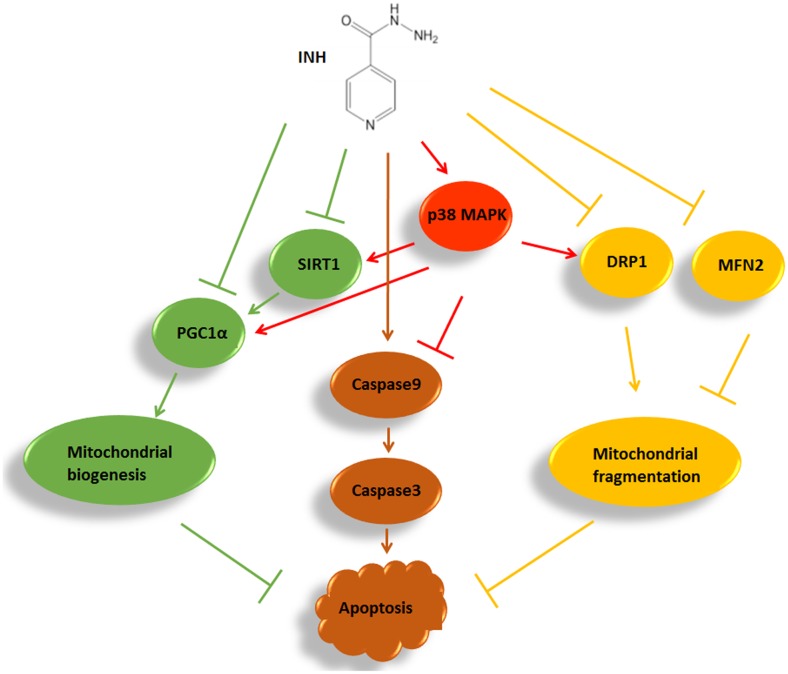
FIGURE 9.
A summary diagram of the pathways involved in INH-induced mitochondrial toxicity. In HepG2 cells, INH inhibited mitochondrial biogenesis, caused mitochondrial fragmentation and exerted apoptotic effects. Meanwhile, INH activated p38 MAPK which not only reduced impairment of mitochondrial biogenesis through partly recovering SIRT1-PGC1α pathway activation, but also promoted protective mitochondrial fission by partial recovery of DRP1 protein expression. Therefore, INH-activated p38 MAPK alleviated apoptotic effects. The effects of INH on SIRT1-PGC1α pathway and DRP1 resulted from the imbalance of many positive and negative roles of upstream pathways. In the study, p38 MAPK was an upstream positive regulator of SIRT1-PGC1α pathway and DRP1. Due to its limited positive effects, p38 MAPK activation failed to completely recover the SIRT1-PGC1α pathway and DRP1 expression. Consequently, although p38 MAPK was activated by INH, the activations of SIRT1-PGC1α pathway and DRP1 were still down-regulated in INH-treated HepG2 cells.