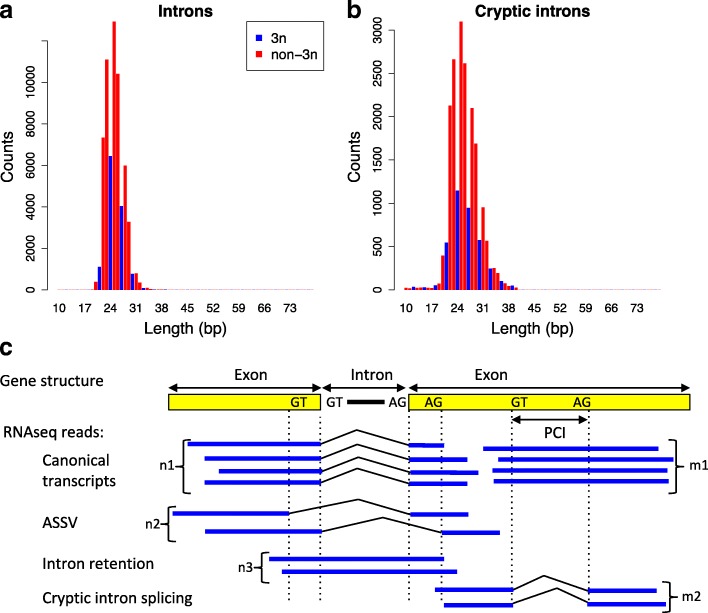
Fig. 1.
Introns and cryptic introns in P. tetraurelia. a Length distribution of introns (n = 65,159). b Length distribution of cryptic introns (n = 20,719 cryptic introns detected in wild-type or NMD-deficient cells). Introns and cryptic introns of length multiple of three (3n) or non-multiple of three (non-3n) are displayed in blue and red, respectively. c Quantification of splicing variation. For each intron, we identified all RNA-seq reads spanning both flanking exons and counted the number of reads corresponding to the canonical transcript (n1), to usage of 5′ or 3′ alternative splice sites (ASSV, n2), and to IR (n3). The IR rate is defined as n3/(n1 + n2 + n3), the ASSV rate is n2/(n1 + n2 + n3). Similarly, for potential cryptic introns (PCIs), the splice rate is defined as m2/(m1 + m2)