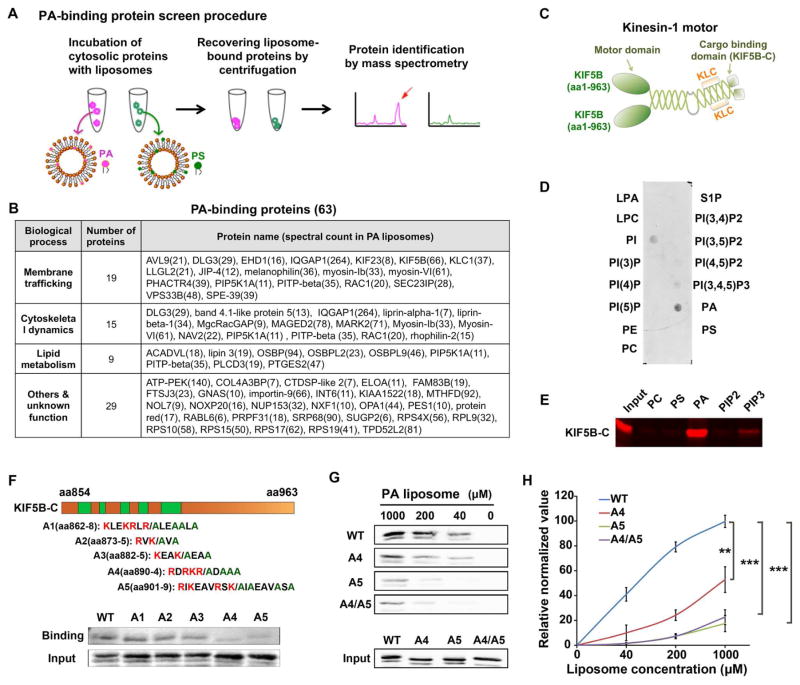
Figure 5.
KIF5B binds to PA directly and specifically. (A) The screening strategy for PA-binding proteins. (B) PA-biding proteins identified by liposome pulldown followed by mass spectrometry. The number in the brackets next to protein names indicates the spectral counts. (C). Domain structure of a kinesin-1 motor protein that composed of two KIF5B and two kinesin light chain (KLC). The C-terminus of KIF5B (KIF5B-C) is the cargo-binding domain. (D). The purified C-terminus of KIF5B (KIF5B-C) specifically bound to PA, and to a less extent to other phospholipids in a lipid strip binding assay. (E) The purified KIF5B-C specifically bound to PA in a liposome pulldown assay. KIF5B-C bound to liposomes containing indicated phospholipids was detected by Western blot using a GST antibody. (F) Identification of the PA-binding sites on KIF5B using saturated liposomes (1 mM). Up, candidate PA-binding sites on KIF5B-C and corresponding alanine mutants. Low, Western blot analysis of PA binding ability of KIF5B-C wild-type and mutants. (G) Identification of A5 as the key PA-binding site on KIF5B using serially diluted liposomes. The mutant A4/A5 did not further reduce the PA-binding of KIF5B. (H) Quantitation of PA binding results in G. n=3. Quantifications are presented as mean ± SD; t-test, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. See also Figure S5 and Tables S1–S3.