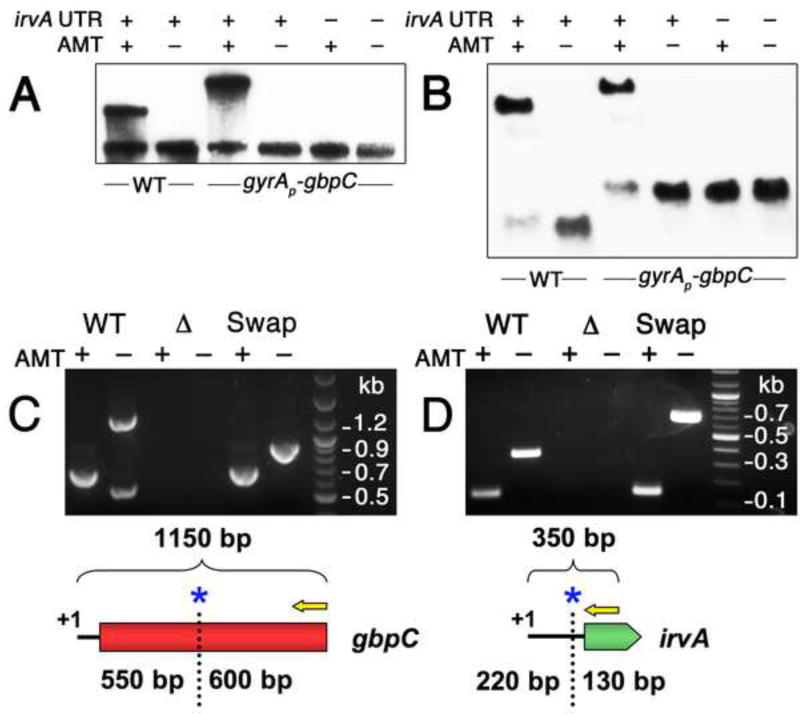
Fig. 4. irvA and gbpC RNAs form a complex during stress.
A) Samples were grown in the presence or absence of AMT RNA crosslinking agent and then detected with anti-gbpC probes via northern blot. The role of the irvA 5’ UTR was assessed by engineering a small deletion within a critical portion of the 5’ UTR required for DDAG. B) The same experiment is performed as in 4A, except an irvA CDS probe is used for the wild-type samples and a gfp CDS probe is used for the gyrAP-gbpC samples. Both probes were mixed in a single hybridization reaction. In panels C and D, the RACE walk procedure was used to probe the interaction region between irvA and gbpC. In both experiments, the entire procedure was repeated using mutant strains containing swapped irvA and gbpC interaction domains. The RACE walk results are also illustrated below each set of reactions. Yellow arrows represent 5’ RACE primers and blue asterisks mark the locations of the first crosslink sites. C) Anti-irvA oligonucleotides are used to precipitate RNA complexes with gbpC. 5’ RACE is performed on gbpC. D) Anti-gbpC oligonucleotides are used to precipitate RNA complexes with irvA. 5’ RACE is performed on irvA. See also Figures S1 and S3.