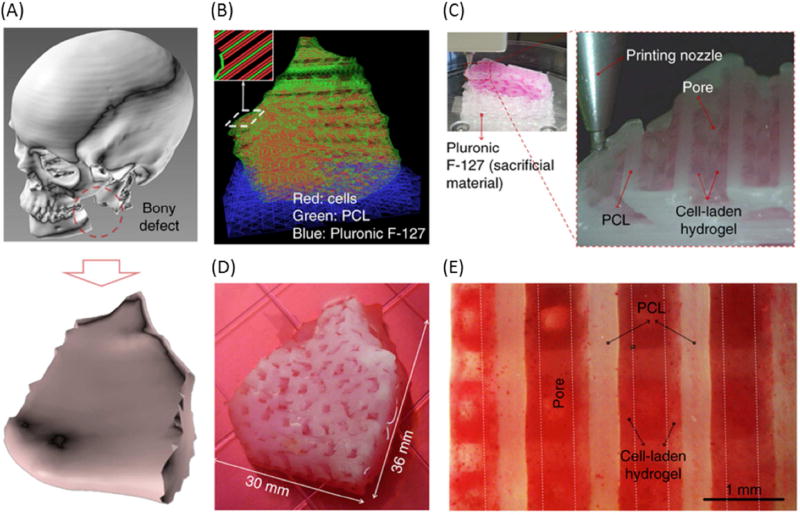
Figure 4.
3D bioprinted human scale mandible and calvarial bone constructs. (A) 3D CAD model of mandible bony defect obtained by converting the medical CT scan data. (B) Visualized motion program depicting the required dispensing paths of cell-laden hydrogel (red), a mixture of PCL and tricalcium phosphate (green), as a scaffold, and Pluronic F127 (blue), which is used as a temporary support structure. (C) 3D patterning of cell laden hydrogel on PCL platform. (D) Macroscopic image of the 3D printed mandible bone defect construct, grown in osteogenic medium for 28 days. (E) Alizarin Red S staining indicates terminal osteogenic induction and mineral deposition in human amniotic fluid–derived stem cell.
From Kang HW, Lee SJ, Ko IK, et al. A 3D bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity. Nat Biotechnol 2016; 34(3): 312–319; with permission.