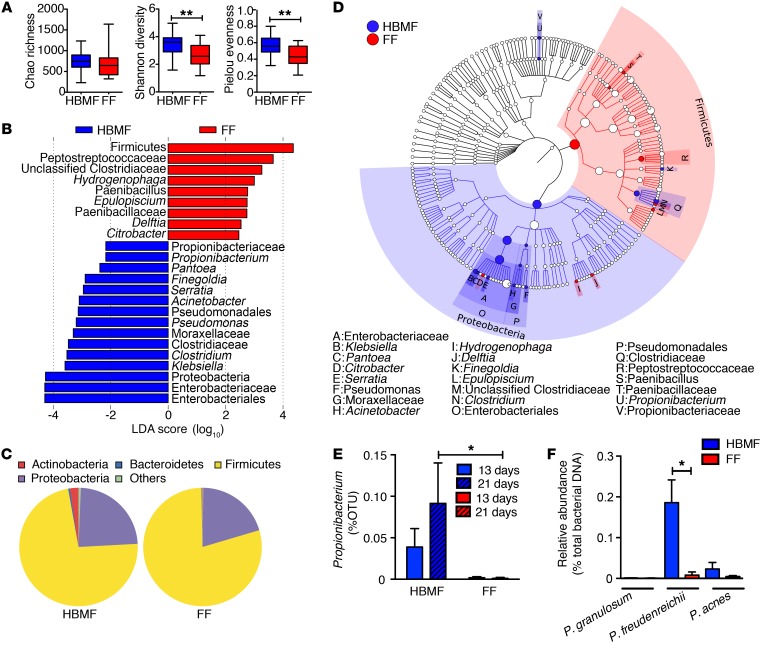
Figure 1. Abundance of Propionibacterium in the fecal samples of HBMF preterm infants.
Fecal samples were collected from HBMF (n = 20) and FF preterm infants (n = 20), and microbiota composition was analyzed by 16S rDNA sequencing. (A) Summary box plots of Chao richness, Shannon diversity, and Pielou’s evenness indices derived from analyses of fecal samples of HBMF (blue) and FF (red) preterm infants on day 13 ± 2 to 3. (B) Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) of taxons between HBMF and FF preterm infants’ microbiota on day 13 ± 2 to 3. Taxa enriched in HBMF preterm infants’ microbiota have a negative score (blue), and taxa enriched in FF preterm infants’ microbiota have a positive score (red). Only taxa with an absolute value of LDA score of more than 2 are shown. (C) Phylum structure of the abundant bacteria in fecal samples of HBMF and FF preterm infants on days 21 ± 3. (D) Taxonomic cladogram of HBMF versus FF preterm infants’ bacterial fecal samples on day 21 ± 3 (blue, HBMF-enriched taxa; red, FF-enriched taxa). (E) Percentage of operational taxonomic units (OTUs) of Propionibacteria in the fecal samples of HBMF and FF preterm infants by day 13 ± 2 to 3 and day 21 ± 3. (F) Relative abundance of different Propionibacteria (e.g., P. freudenreichii) in fecal samples of HBMF and FF preterm infants. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, 2-tailed unpaired t test (A, E, and F). Kruskal-Wallis test (B and D).