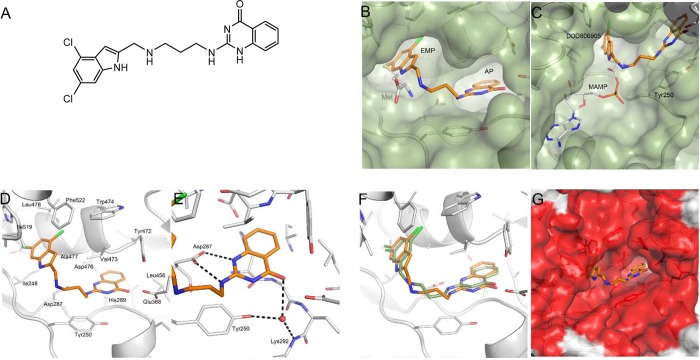
Figure 2.
DDD806905 binding mode. (A) DDD806905 was identified as our lead LdMetRS inhibitor, with an IC50 of 94 nM. (B) Crystal structure of TbMetRS:DDD806905 (PDB 5NFH). DDD806905 bridges the expanded methionine pocket (EMP) and the ligand stabilized auxiliary pocket (AP). The dichloroindole moiety occupies the same site as methionine (C atoms gray). The solvent accessible surface of TbMetRS:DDD806905 is shown in dark green. (C) Comparison of the binding mode of DDD806905 (C atoms gold) compared to TbMetRS:methionyl adenylate (MAMP, C atoms gray, PDB 4EG3). (D) Binding mode of TbMetRS:DDD806905 showing protein side chains that line the binding site. (E) H-bond interactions between quinazolinone moiety of DDD806905 and residues lining the auxiliary pocket. H-bond interactions are shown as dashed lines and water molecules as red spheres, and key residues are labeled. (F) The binding modes of DDD806905 (C atoms gold) compared with aminoquinolone ligand Chem 1312 PDB 4EG5 (C atoms green). (G) Sequence conservation is high between TbMetRS and LdMetRS around the DDD806905 binding site with identical residues colored red and nonidentical colored gray.