Figure 5. Schematic representation of the metabolic pathways linked to everolimus treatment.
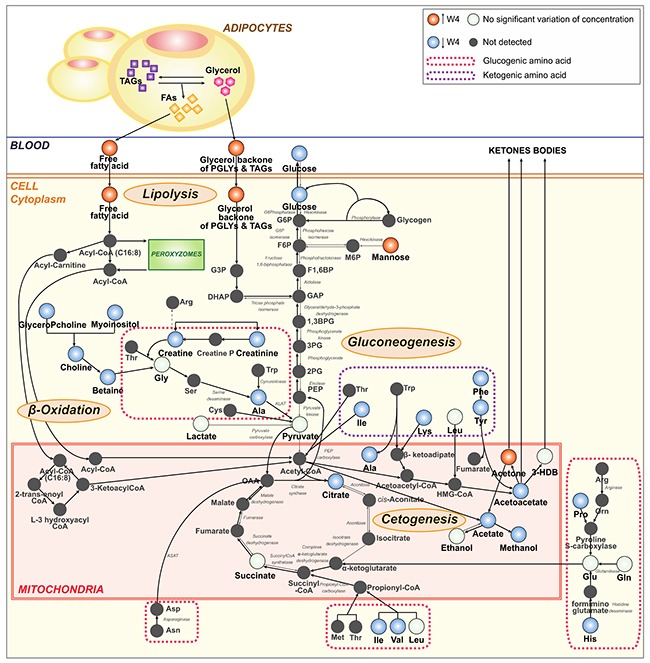
The administration of the everolimus and trastuzumab combination, particularly of the mTOR inhibitor, in patients with HER-2+ breast cancer alters the serum host metabolome. Everolimus activates the lysis of TAGs in the adipocytes and the release of free FAs in the bloodstream. In addition, the inhibitor of mTOR promotes β-oxidationand ketogenesis. These different metabolic processes are amplified by the fasting status of patients at the time of sampling. The discussion details evidence underlying this model. The therapy empties the liver and muscle glycogen stores resulting in the decrease of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. In fasting conditions, HER-2+ breast cancer patients are no longer able to maintain their blood glucose levels to reference values. The continued use of amino acids, during and after treatment, leads to a decreased gluconeogenesis. Black arrows represent the chemical reactions activated by everolimus. Red circles correspond to metabolites whose concentration are higher at W4 than at baseline. Blue circles represent metabolites with lower concentrations at W4 compared to W0, while white circles correspond to metabolites that do not vary over the intervention. 1,3BPG: 1,3-biphosphoglycerate; 3-HDB: 3-hydroxybutyrate; 2PG: 2-phosphoglycerate; 3PG: 3-phosphoglycerate; Ala: alanine; Arg: arginine; Asn: asparagine; Asp: aspartate; Creatine P: creatine phosphate; Cys: cysteine; DHAP: dihydroxyacetone phosphate; FA: fatty acid; F1,6BP: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; F6P: fructose-6-phosphate; GAP: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; G3P: glycerate-3-phosphate; GlyceroPcholine: glycerophosphocholine; G6P: glucose-6-phosphate; G6Phosphatase: glucose-6-phosphatase; Gln: glutamine; Glu: glutamate; His: histidine; HMG-CoA: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A; Ile: isoleucine; M6P: mannose-6-phosphate; Met: methionine; Leu: leucine; Lys: lysine; OAA: oxaloacetate; Orn: ornithine; PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate; PGLY: phosphoglyceride; Phe: phenylalanine; Pro: proline; Ser: serine; TAG: triacylglyceride; Trp: tryptophan, Tyr: tyrosine; Val: valine.
