Figure 3. Proposed mechanisms for dnATF5 anticancer activity.
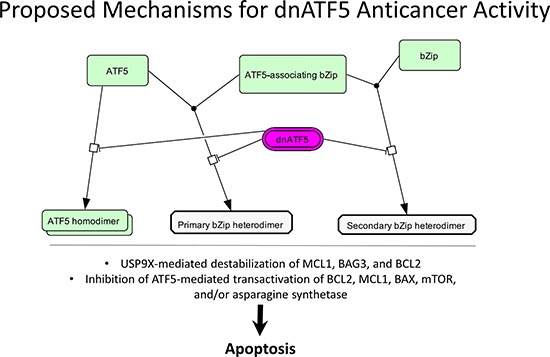
dnATF5 is thought to disrupt ATF5 homo/heterodimerization or homo/heterodimerization of two non-ATF5-interacting bZip transcription factors. This results in USP9x-mediated destabilization of antiapoptotic proteins or inhibition of ATF5-mediated transactivation of BCL2, MCL1, BAX, mTOR, and asparagine synthetase, thereby leading to apoptosis. Image was generated using CellDesigner 4.4 and PowerPoint 2013.
