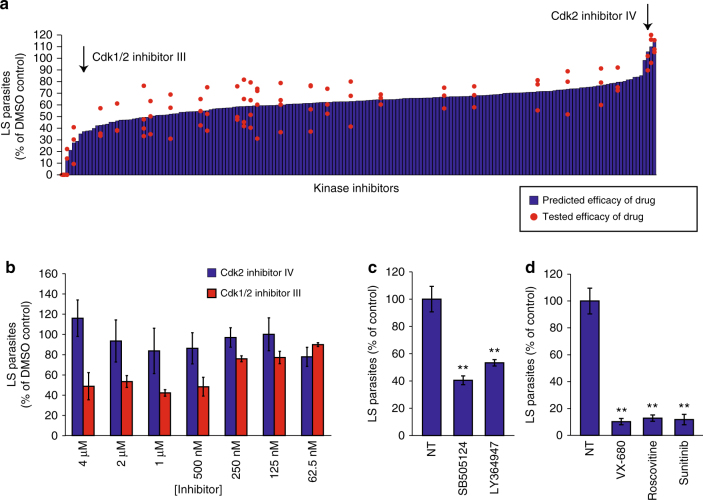
Fig. 4.
Computational prediction of effective host-based drugs against Plasmodium yoelii infection. a Bar graph depicting predicted efficacy of host-targeted kinase inhibitors in eliminating LS parasite burden. Independent experimental data measuring LS inhibition from drugs used to generate the training dataset are overlaid as data points onto the bar graph. Red arrows indicate predicted efficacies of two drugs against the same kinase target—CDK2. b 150,000 Hepa 1–6 cells were infected with 50,000 P. yoelii parasites and then treated with CDK2 inhibitors at different concentrations ranging from 4 μM to 62.5 nM at 1.5 h.p.i. LS burden was evaluated by microscopy at 24 h.p.i. c 150,000 Hepa 1–6 cells were infected with 50,000 P. yoelii parasites and then treated with 500 nM of TGFBR-1 inhibitors SB505124 or LY364947 at 1.5 h.p.i. LS burden was evaluated by microscopy at 48 h.p.i. **p ≤ 0.01 evaluated by Student’s two-tailed t-test. d 150,000 Hepa 1–6 cells were infected with 50,000 P. yoelii parasites and then treated with 500 nM VX-680, Roscovitine or Sunitinib at 1.5 h.p.i. Parasite burden was evaluated by microscopy at 24 h.p.i. **p ≤ 0.01 evaluated by Student’s two-tailed t-test. All data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviation of analytical replicates