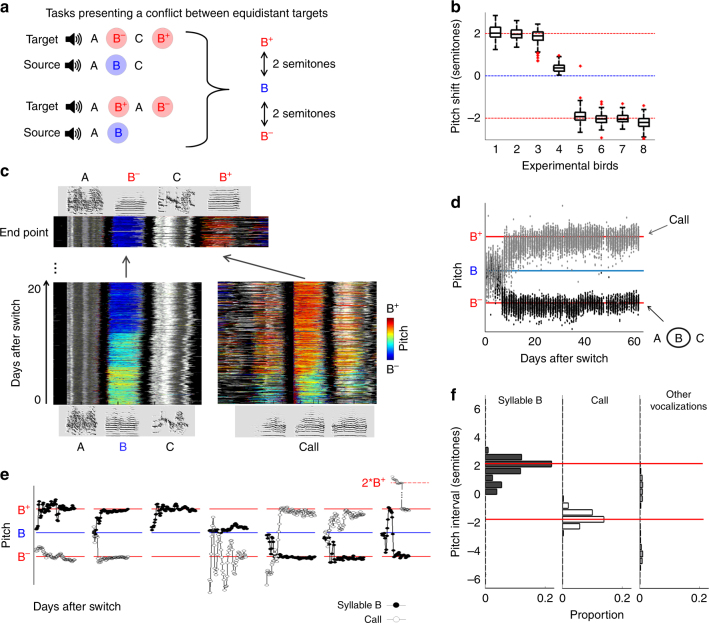
Fig. 5.
Competitive error assignment. a Imitation tasks presenting birds with a conflict between spectrally equidistant targets: ABC → AB−CB+ (imitation task 3, top) and AB → AB+AB− (imitation task 5, bottom). Syllable B in the source songs is presented with the target syllables B− and B+, shifted by 2 semitones down and up respectively. b Boxplots of the pitch shift from source of syllable B renditions on endpoint day, in experimental birds trained with the imitation tasks in a (n = 4, ABC → AB−CB+ n = 4, AB → AB+AB−). Birds are presented in descending order of median pitch shift. In seven out of eight birds, syllable B closely matched either B− or B+. c Developmental trajectory of an experimental bird trained with ABC → AB−CB+. Stack plots as in Figs. 2–4. Syllable B in the song motif shifted down to match target syllable B− (left); in parallel, a call performed outside the song motif differentiated into the missing target B+ (right), and got incorporated into the motif (top). d Median pitch in consecutive renditions of syllable B/B− (black), and the call that shifted to B+ (gray), during development in the same bird. e Pitch trajectories (daily medians) of all other experimental birds trained with the imitation tasks in a. Black circles, motif syllable B; white circles, a vocalization type (typically a call), which shifted towards the vacant target. f, Left, distribution of the absolute pitch distance from source of renditions originating in motif syllable B on endpoint day (0 = pitch of source syllable B; mean per bin across experimental birds, n = 8); middle and right, same for harmonic vocalizations besides motif syllable B, within 6 semitone distance from source; for each bird, pitch distance is normalized by the direction to which syllable B has shifted: positive values for renditions shifted in the same direction as syllable B, and negative values for renditions shifted in the opposite direction. Across birds, no vocalization converged on the target occupied by the motif syllable. A call converged on the vacant target (middle), while all other vocalizations converged on neither of the targets (right)