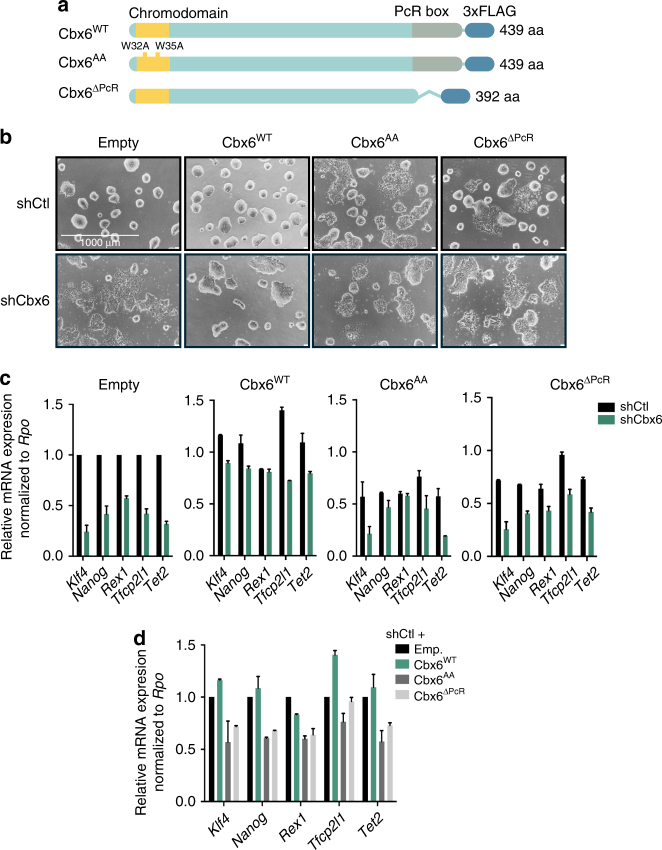
Fig. 2.
CBX6 function depends on its N- and C-terminal domains. a Schematic representation of the CBX6 constructs used in the rescue experiment. Note that every construct contained a silent mutation (not depicted) that conferred resistance to the CBX6 shRNA. b Phase contrast images of different cell lines overexpressing an empty construct or a CBX6WT, CBX6AA, or CBX6ΔPcR construct, additionally infected with shCtl or shCbx6 lentiviral particles. c qRT-PCR analysis of pluripotency genes in the different cell lines. Results are shown relative to empty shCtl and were normalized to Rpo. Error bars represent SD of two independent experiments. d qRT-PCR analysis of pluripotency genes in the shCtl-infected cell lines. Results are shown relative to empty shCtl and normalized to Rpo. Error bars represent SD of two independent experiments