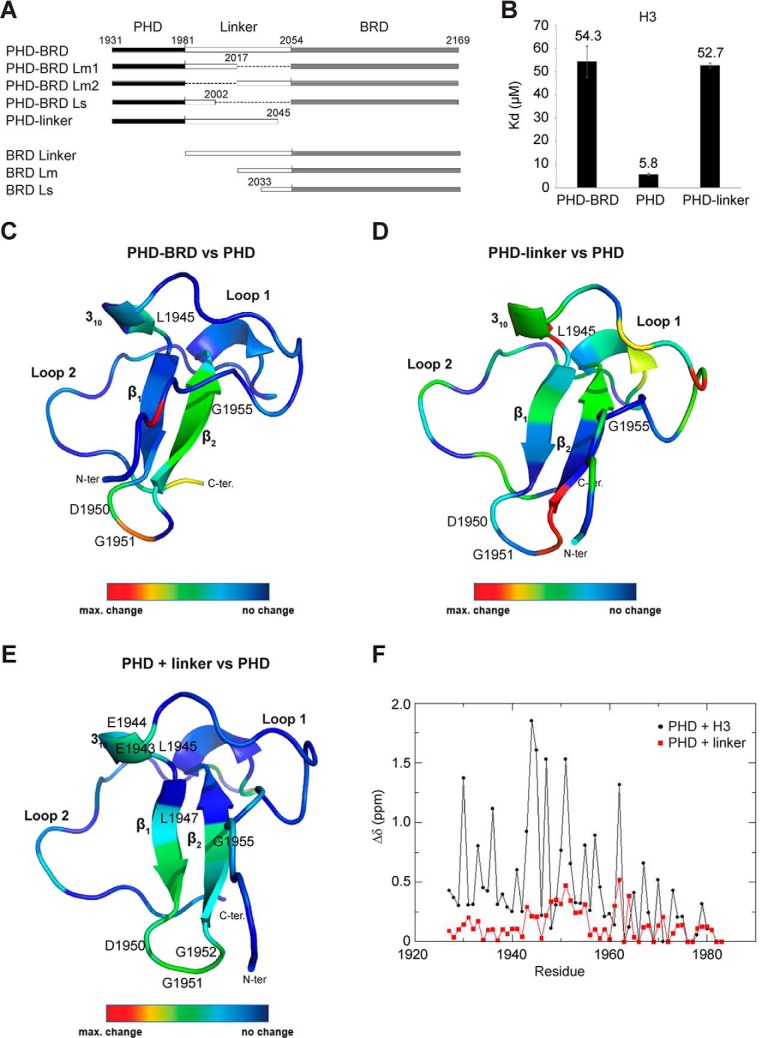
Figure 3.
The interdomain linker modulates the binding affinity of the BAZ2B PHD toward histone H3 by binding to the PHD. A, schematic of all used BAZ2B constructs. B, binding affinities of BAZ2B PHD, the PHD linker, and PHD–BRD toward H3, measured by ITC. Error bars represent mean ± S.D. (n = 4). C and D, differences in chemical shifts between BAZ2B PHD–BRD and the PHD (C) and between the PHD linker and the PHD (D) visualized with a color code. N-ter, N terminus; C-ter, C terminus. E, differences in shifts between the native BAZ2B PHD domain and upon binding of the PHD-proximal linker peptide visualized with a color code. F, chemical shift perturbations (Δδ) for each residue of the 15N-labeled BAZ2B PHD between apo and bound spectra of PHD+H3(1–21aa) (black) and PHD+linker (1982ASGQTLKIKKLHVKGKKTNESKKGKK2007) (red).