Figure 1.
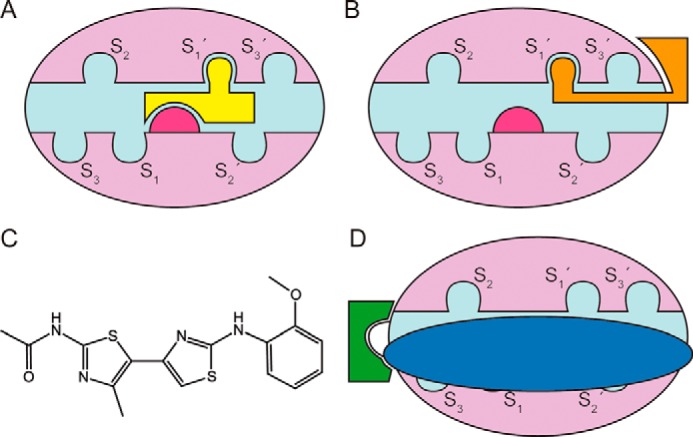
Mechanisms of MMP inhibitors. A, mode of action of initial MMPIs (yellow), which blocked the catalytic zinc ion (magenta) at the bottom of the active-site cleft (cyan). The cleft has subsites upstream (S1, S2, S3,…) and downstream (S1′, S2′, S3′,…) of the metal to accommodate the side chains of substrates. In MMPs, the primary specificity pocket is S1′. B, mode of action of current small-molecule MMPIs, which mostly bind to S1′ and/or exosites rather than the zinc. C, the chemical structure of compound JNJ0966. D, a novel approach by Scannevin et al. (9), in which the MMPI (green) targets the final activation point of the zymogen and prevents prodomain (blue) removal. This MMPI does not inhibit the mature MMP.
