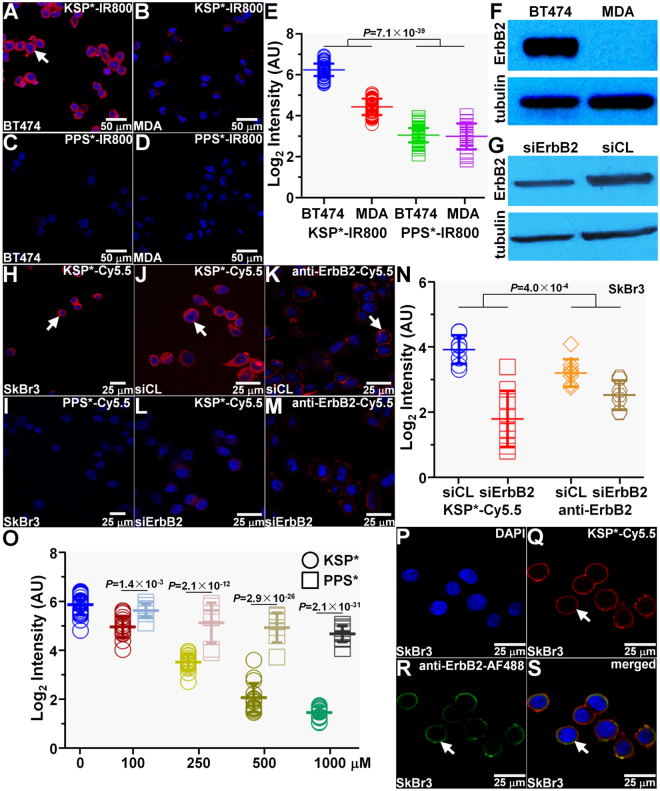
Figure 2.
Specific peptide binding to ErbB2. KSP*-IR800 shows (A) strong staining to the surface (arrow) of BT474 human breast cancer cells but not to that for (B) MDA-MB-231. (C,D) Scrambled control peptide PPS*-IR800 shows minimal binding to either cell. (E) Quantitative comparison is shown in log2 scale. We found 3.55-fold greater signal for KSP*-IR800 with BT474 versus MDA-MB-231 cells but only a 1.04-fold difference with PPS*-IR800. Using an ANOVA model fit with terms for 4 means to log-transformed data, we found the difference of differences to be significant. Western blot analysis shows ErbB2 expression for (F) BT474 and MDA-MB-231 cell and for (G) SKBR3 human breast cancer cells transfected with siErbB2 targeting siRNA (knockdown) and siCL non-targeting siRNA (control). (H,I) Use of a Cy5.5 label produces results to that found for IRDye800 with SKBR3 cells. (J,K) KSP*-Cy5.5 and anti-ErbB2-Cy5.5 bind significantly greater to the surface (arrows) of siCL (control) SKBR3 cells compared with that for (L,M) siErbB2 (knockdown) cells. (N) We found 4.42-fold greater signal for KSP*-Cy5.5 with siCL treated SkBr3SKBR3 control cells compared with that for siErbB2 knockdown cells and 1.60-fold greater intensities with anti-ErbB2-Cy5.5. Using an ANOVA model, we fit with terms for 4 means to log-transformed data, and found the difference of differences to be significant. (O) On competition, we found the mean fluorescence intensity with KSP*-Cy5.5 to SKBR3 cells decreases significantly in a concentration dependent manner with addition of unlabeled KSP*. By comparison, binding was significantly less affected with addition of unlabeled PPS*. We used a one-way ANOVA to compare the mean intensities, and show P-values at each concentration. (P–S) Binding of KSP*-Cy5.5 (red) and anti-ErbB2-AF488 (green) co-localizes to the surface (arrows) of SKBR3 cells with a Pearson’s correlation coefficient of ρ = 0.70. Each result is an average of 3 independent measurements.