Figure 4.
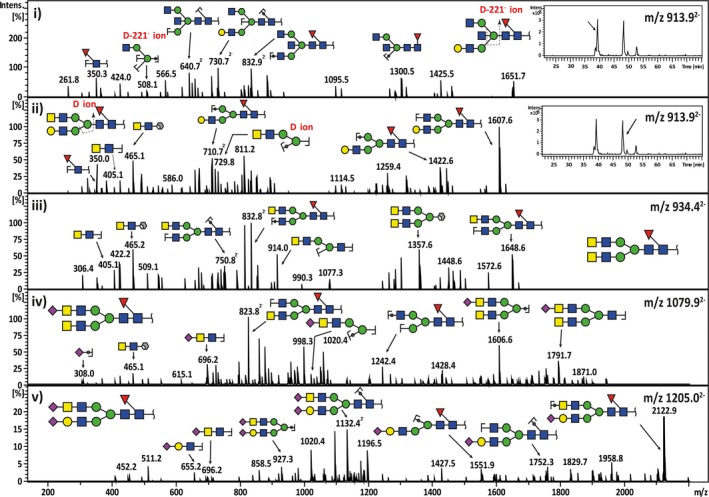
Representative MS 2 fragment ion spectra depicting the characterization of bisecting‐biantennary and LacdiNAc‐type N‐glycan structures in serous cancers. The neutral N‐glycan m/z 913.92− with a composition of (Hex)1(HexNAc)3(dHex)1 +(Man)3(GlcNAc)2 consists of two compositional isomers with separate retention times (i‐insert). The first isomer was shown to elute at 38.5 min and the tandem MS spectra corresponded to a bisecting GlcNAc‐type core‐fucosylated N‐glycan with a monosaccharide composition of (Gal)1(GlcNAc)3 (Fuc)1+(Man)3(GlcNAc)2. This was confirmed by the presence of the diagnostic D‐221− cleavage ion at m/z 508.11−. The second‐eluting isomer at 48 min consisted of a monosaccharide composition of (Gal)1 (GalNAc)1 (GlcNAc)2(Fuc)1+(Man)3(GlcNAc)2, which corresponded to a ‘LacdiNAc’‐type N‐glycan (ii‐insert). The presence of the LacdiNAc antenna (GalNAcβ1‐4GlcNAc) was indicated by the B ion at m/z 405.11− and the 1,3A cross‐ring cleavage ion at m/z 465.11− (‘F ion’). Several forms of LacdiNAc‐type N‐glycans identified in serous ovarian cancer are illustrated for neutral LacdiNAc N‐glycan with m/z 934.42− (iii), sialylated LacdiNAc N‐glycan with m/z 1079.92− (iv) and sialylated LacdiNAc/LacNAc N‐glycan with m/z 1205.02− (v).
