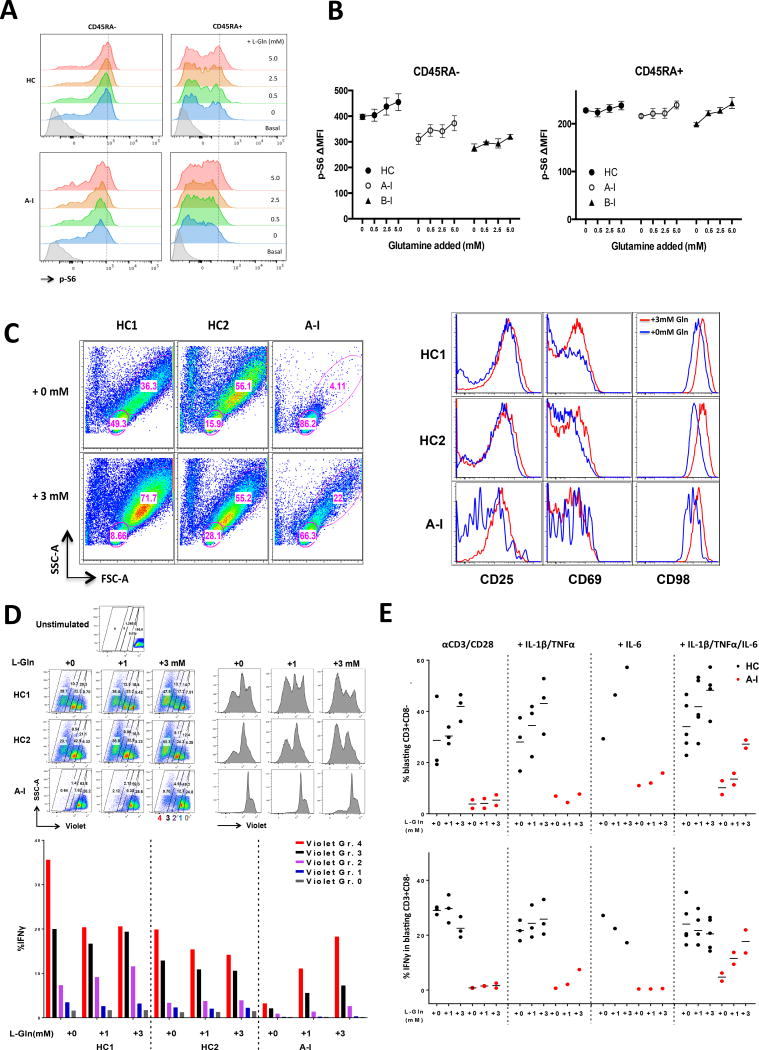
Figure 6. Glutamine supplementation in combination with cytokines can partially restore the TCR-induced proliferation and IFN-γ defects in a CARD11mut patient.
(A) Improved phospho-S6 activation by PMA after addition of glutamine. PBMC from the HC and CARD11 patient were rested in media then PBS supplemented with glutamine (L-Gln) and stimulated with PMA. Phospho-S6 was measured by intracellular flow cytometric staining of CD4 CD45RA- memory and CD45RA+ naïve T-cells. The dashed line indicates the maximum phospho-S6 activation peak (MFI) by PMA with 5mM glutamine addition in HC. (B) ΔMFI plot (PMA treated vs. untreated) for phospho-S6 in (A) (HC, n=5; three independent experiments for A-I and two for B-I; mean±SEM). (C) Left: Increased proliferation of CD4+ naive T cells isolated from patient A-I patient in serum-free medium stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 and cytokines (IL-1β, TNFα, and IL-6) for 5 days with glutamine supplementation. Right: Increased surface activation marker expression with glutamine addition plus cytokines in patient A-I (gated on FSChiSSChi blasts from the left panel). Data are representative of three experiments. (D) Top: Impaired naive CD4+ T cell proliferation was partially restored by anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation with excess glutamine and cytokines IL-1β, TNFα, and IL-6 in patient A-I. Bottom: Rescue of IFN-γ expression was proliferation dependent. Dividing cells were gated into four groups based on CellTrace Violet intensity (top left), and IFN-γ was measured by intracellular staining in each group (bottom). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (E) Quantification of the percentage of proliferative CD3+CD8− blasts (top), and the percentage of IFNγ-producing CD3+CD8− blasts (bottom) with the treatments by increasing glutamine concentration. Data combined of the experiments: αCD3/CD28: HC (n=3), A-I (n=2); +IL1β/TNFα: HC (n=3), A-I (n=1); +IL-6: HC (n=1), A-I (n=1); + IL1β/TNFα/IL-6: HC (n=5), A-I (n=2).