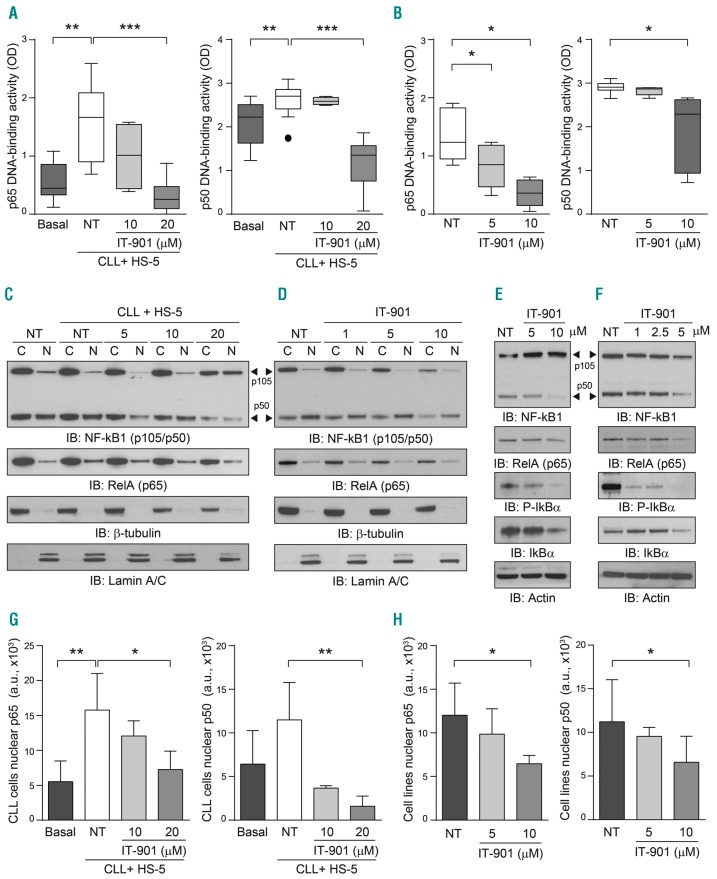
Figure 1.
IT-901 blocks nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activity in primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells and derived cell line. (A) DNA binding activity of the p65 and p50 subunits in primary CLL cells (n=13) was analyzed using an ELISA kit, applying the same amount of nuclear extracts. Leukemic cells were co-cultured on a stromal layer (HS-5) to maximize the activation of the pathway, in the presence of increasing doses of drug or vehicle (NT) for 6 hours (h). (B) Cumulative DNA binding activity of NF-κB (p65 and p50) in 2 different cell line models of CLL, Mec-1 (n=5), and OSU-CLL (n=3). (C, D, G and H) Cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions obtained from primary CLL cells (C) or cell lines (D) cultured as indicated above were resolved by SDS-PAGE and blotted with specific antibodies to detect the expression of NF-κB1 subunits p105/p50 (arrow head) and RelA (p65). Lamin A/C and β-tubulin were used as nuclear and cytoplasmic markers, respectively. Nuclear p65 and p50 band intensities in primary CLL samples and CLL cell lines are reported in (G) and (H), respectively. (E and F) Total lysates from primary CLL cells (E) or CLL cell lines (F) cultured alone and exposed to different doses of IT-901 or vehicle (NT) for 6 h were resolved by SDS-PAGE and expression of the NF-κB complex analyzed using specific antibodies. Actin was used as a loading control. OD: optical density.