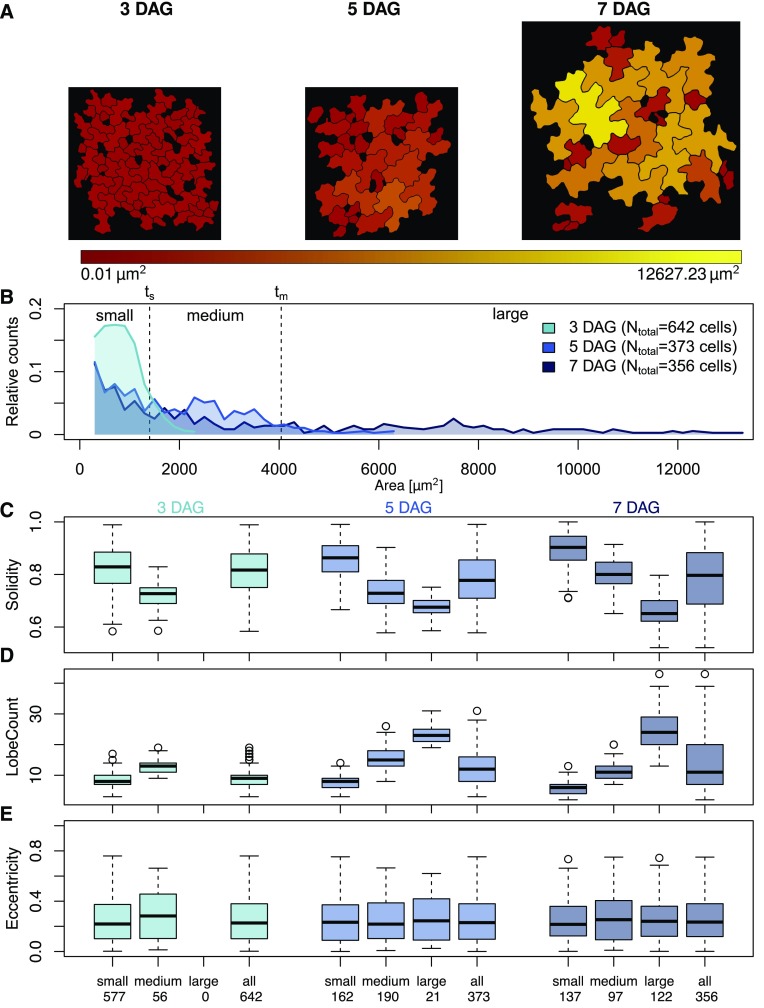
Figure 5.
Analysis of pavement cell shape characteristics during development. A, Epidermal pavement cell shape in the adaxial side of cotyledons from wild-type (Col-0) seedlings 3, 5, and 7 DAG. The color gradient represents the area of the detected cells (red, small to yellow, large). B, Relative distribution of cell areas in cotyledons of 3-, 5-, and 7-d-old seedlings. Cells were categorized into small cells (threshold ts ≤ 1400 µm2, which includes 90% of the cells in 3-d-old seedlings), medium-sized cells (threshold tm ≤ 4042 µm2, which includes 90% of the cells in 5-d-old seedlings that exceed ts), and large cells (≥tm), which represent the different stages of cell differentiation. C to E, Quantification of cell shape features during differentiation. Cells were grouped according to (B) or treated as a single input set (all). Numbers on the x axis refer to the number of cells analyzed per sample set. Feature values are shown in box plots. Results are medians; boxes range from first to third quartile. For a summary of all features and statistical analysis of feature values, see Supplemental Figure S5. (C) Solidity decreases with increasing cell size and differentiation, which is consistent with (D) an increased number of lobes, while other parameters, as shown for (E) eccentricity are largely unaffected during differentiation.