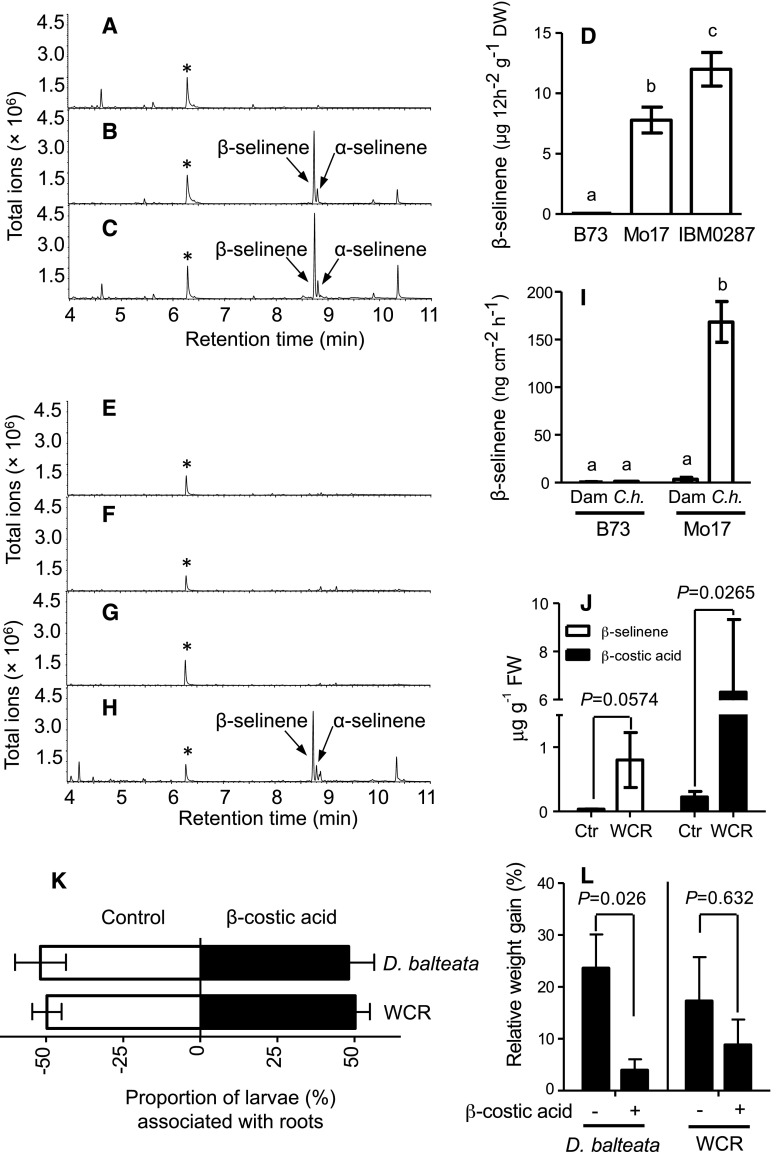
Figure 2.
β-Selinene can exist as a dominant elicited volatile, and the pathway product β-costic acid can reduce herbivore performance. A to C, Representative GC coupled with flame ionization detection (FID) traces of volatile emissions collected from live roots of field-grown maize lines B73 (A), Mo17 (B), and IBM-RIL-0287 (C) 20 d after pollination. D, Average (n = 4; ±se) quantity (μg 12 h−1 g−1 dry weight [DW]) of β-selinene volatiles emitted from respective maize roots. E to H, Representative GC-FID traces of emitted volatiles collected from living control B73 (E), C. heterostrophus-infected B73 (F), control Mo17 (G), and Mo17 C. heterostrophus-infected (H) stems. I, Average (n = 4; ±se) quantity (ng cm−2 h−1) of β-selinene emitted as a volatile from the stems of 5-week-old plants following damage and treatment with water (Dam) or with 100 μL of 1 × 107 spores C. heterostrophus (C.h.). Within plots D and I, different letters (a–c) represent significant differences (all ANOVAs, P < 0.05; Tukey’s test corrections for multiple comparisons, P < 0.05). J, Average (n = 4; ±se) root tissue concentrations (μg g−1 fresh weight [FW]) of β-selinene and β-costic acid levels in the roots of IBM-RIL-0287 following 17 d of either no treatment (Ctr) or herbivory by WCR larvae (Student’s t test, one-tailed distribution, equal variance). K, Average WCR (n = 18; ±se) and D. balteata (n = 57; ±se) preference over 4 h for excised maize roots treated with either ethanol:water (15:85) alone (Control) or the same solution containing β-costic acid to achieve a root tissue concentration of 100 μg g−1 fresh weight. Each replicate (n) consisted of assays with five individual third instar larvae where distributions were measured at 30, 60, 90, 120, 180, and 240 min and collectively averaged (Student’s t test, P > 0.05). L, Average (n ≥ 5, ±se) performance (percentage relative weight gain) of third instar WCR and D. balteata larvae over 2 d of feeding on root tissues with (+) and without (−) additions of β-costic acid as described in the preference study (two-way ANOVA, P < 0.05).