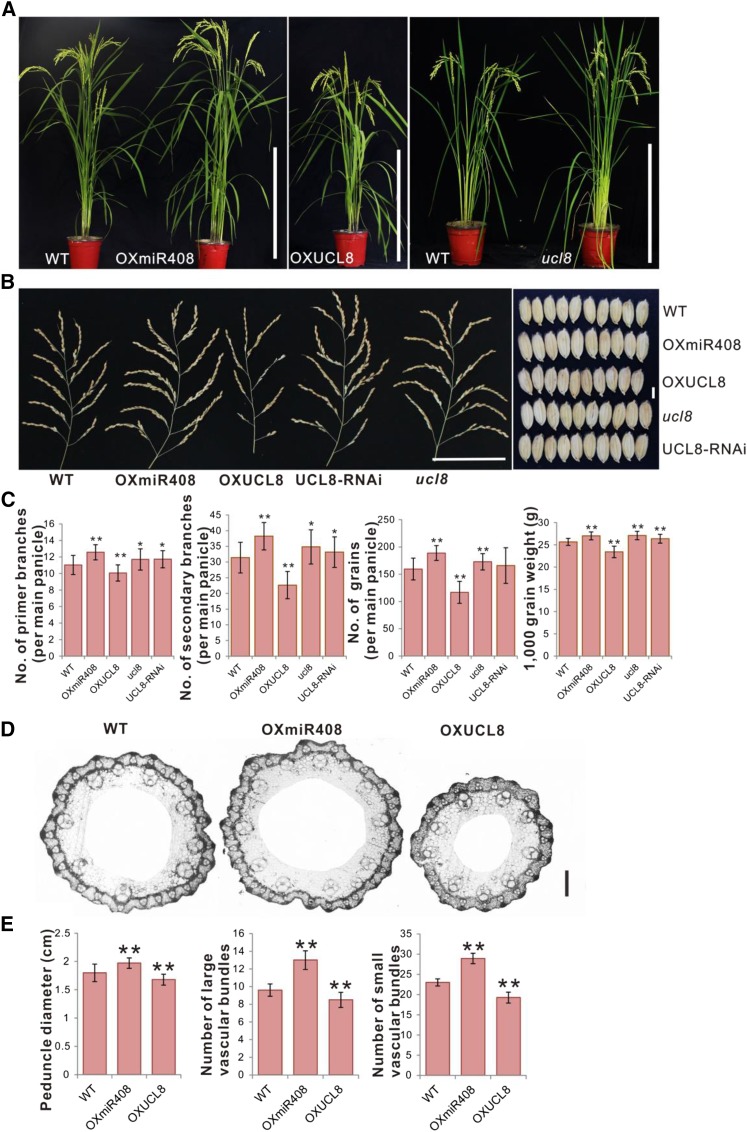
Figure 1.
Phenotypes of OXmiR408, OXUCL8, ucl8, and UCL8-RNAi transgenic rice plants. A, Gross morphology of wild-type (WT), OXmiR408, OXUCL8, ucl8, and UCL8-RNAi transgenic plants. Bars = 40 cm. B, Panicle and grain morphologies of the wild-type and transgenic plants. Bars = 10 cm for the panicles and 3 mm for the grains. C, Number of primer branches per main panicle, number of secondary branches per main panicle, number of grains per main panicle, and 1,000-grain weight of the wild-type plants and the transgenic plants. Values are expressed as means ± sd (n = 30 plants). Significant differences were identified at the 5% (*) and 1% (**) probability levels using Student’s t test. D, Cross sections of peduncles in wild-type, OXmiR408, and OXUCL8 plants. Bar = 500 µm. E, Comparison of the peduncle diameters, number of large vascular bundles, and small vascular bundles in wild-type, OXmiR408, and OXUCL8 plants. Values are expressed as means ± sd (n = 15 plants). Significant differences were identified at the 1% (**) probability level using Student’s t test.