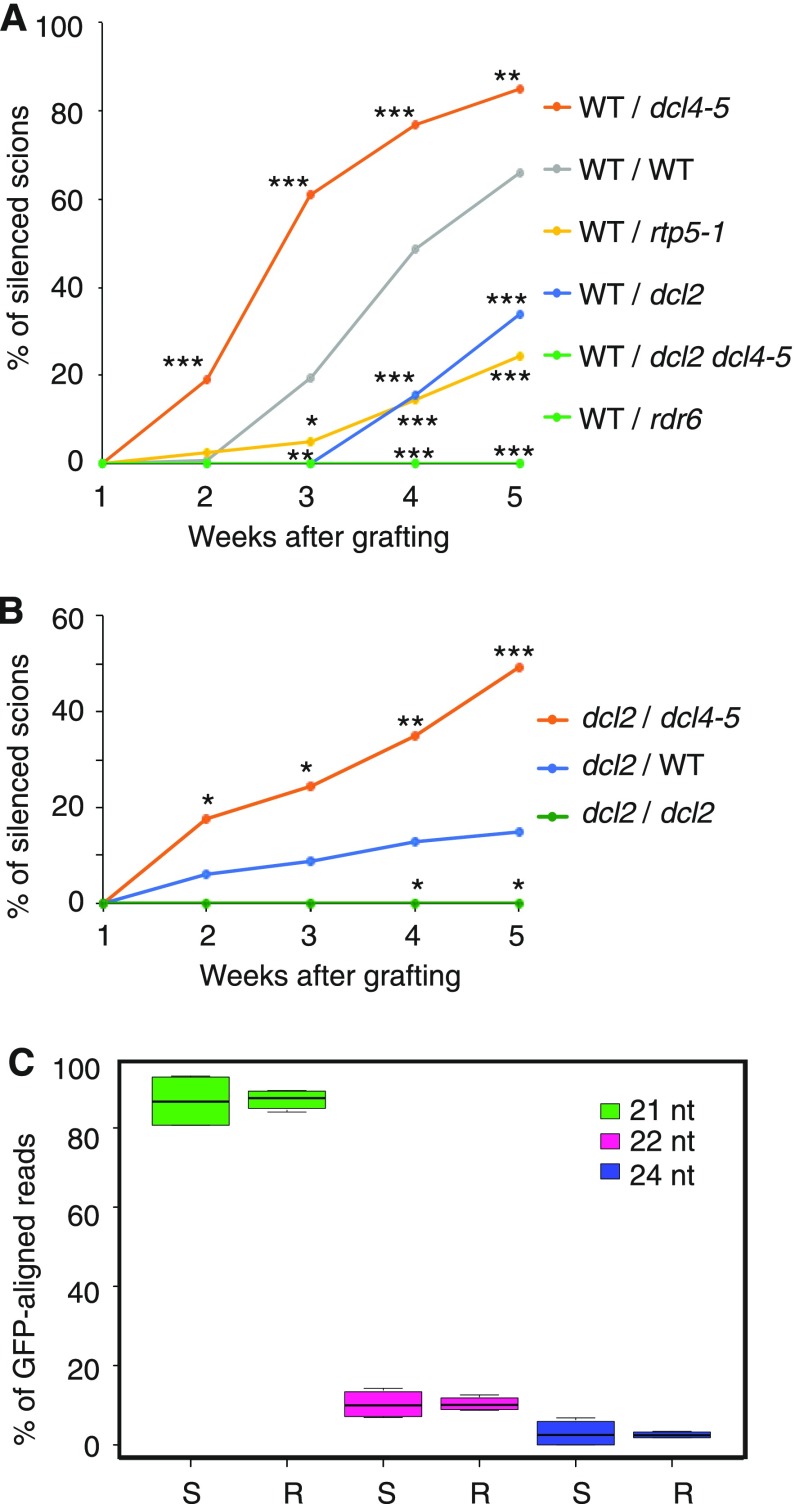
Figure 4.
DCL requirements in rootstocks and scions for the transmission and reception of systemic, RDR6-dependent PTGS. A, The transmission of PTGS is compromised from dcl2 rootstocks but enhanced from dcl4 rootstocks. Wild-type (WT) scions expressing GFP (transgenic line 214) were grafted onto 10027-3 wild-type and mutant rootstocks. All 10027-3 lines were homozygous for the 10027-3 T-DNA locus. In total, 39 to 129 grafted plants were assessed over at least three independent experiments for each combination of genotypes. P values for pairwise comparison of each treatment with wild-type/wild-type grafts are indicated for 2 to 5 weeks postgrafting. B, Reception of PTGS is compromised in dcl2 scions but enhanced by grafting dcl2 scions onto dcl4 rootstocks. 10027-3 dcl2 (Kas-1) scions were grafted onto 10027-3 wild-type, dcl4-5, or dcl2 (Kas-1) rootstocks. Scions of self-grafted 10027-3 dcl2 (Kas-1) control plants showed no silencing. In total, 38 to 101 grafted plants were assessed over at least three independent experiments for each combination of genotypes. P values for pairwise comparison between dcl2/wild type and dcl2/dcl4-5 or dcl2/dcl2 are indicated for 2 to 5 weeks postgrafting. In A and B, plants were transferred to soil 1 week after grafting; GFP silencing in shoots was monitored every week and is expressed as a percentage of the total number of scions. Statistical analysis was performed using Fisher’s exact tests followed by Benjamini and Hochberg multiple correction (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001). dcl2 refers to the dcl2 (Kas-1) allele, and rdr6 refers to the sde1-1 allele. C, Size distributions of GFP-specific siRNAs in floral buds of nontransgenic scions grafted onto 10027-3 rootstocks (S) and in 2-week-old 10027-3 roots used for grafting (R). The data are based on eight small RNA libraries (nscion = 4, nrootstock = 4). Nontransgenic scions were grafted onto either 10027-3 wild-type (n = 2) or rdr6 (n = 2) rootstocks. The GFP-specific siRNA profiles for these roots are shown in Supplemental Figure S5. Box plots were generated based on the percentage of each GFP-aligned siRNA size class relative to all GFP-aligned sRNA size classes (21, 22, and 24 nucleotides) for each sample. Combined analysis of the eight small RNA libraries showed that there was no difference in the relative abundance of each siRNA size class in the scion or rootstock tissues analyzed.